Welcome to IRIS Publishers! Here you can read from our vast archive of scientific knowledge that we’ve collected from all over the world.
Thursday, November 28, 2019
Wednesday, November 27, 2019
Iris Publishers-Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology | Iris Publishers-Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology
Authored by Da Yong Lu
Abstract
Nursery service is the main part of healthcare efforts worldwide. Patient’s recovery and survivals need high quality nursery to support and promotions. In this editorial, many pathways, like education improvements, medical knowledge for nurses and willing to take parts of more responsibility from nursery care are addressed.Keywords: Healthcare; Nursing; Medical service; Modern technology; Mathematicians; Psycho-analysis
Introduction for Nursery Service Worldwide
Today, a half of major diseases are chronic diseases. Their recovery processes are not defined in operation-room (surgery). But, getting better in the bedside (therapeutic conventions— drugs, nutrition, instruments and nursery). A great proportion of healthcare services are both doctors and nursing [1-7]. Any unilateral activity may compromise medication quality. The promotion of the quality and scope of nursing activity is especially important for medical study and practices. However, current nursing activities in hospitals does not receive enough academic respects globally.Requirement for High Quality Nursery
There is no nursery knowledge that can be applied on every medical discipline. Nursery education plays key role for clinical nursery practice [8,9].System developments for nursery services and education are indispensable [10]. This educational difference requires efforts among teachers and nurses. Good teamwork and cooperative efforts can provide better nursery services [11-13]. Therapeutics in the future is no longer a performance and decision-making by doctors alone. Many technical or assistance forces will take part of medical practice for quality boosting-including pharmacologists, pathologists, biochemical technologists, nurses, mathematicians and many others [11-13]. Without the assistance of these experts, clinical doctors will be narrow-minded and difficult to execute best therapeutics for all patients.
Medical Services in Different Areas
In summary, different types of nursery play key roles in clinical trials, especially chronic diseases, such as HIV/AIDS treatments [14], mental diseases [15-18], bone disorders [18-21], metabolic diseases [22-27], cancers [28,29] and so on. To promote medical practice, nurses must play very important responsibility in medical treatments.Feedback from Nurses
If a doctor makes mistake in patient’s treatment, nurses must report these mistakes to regulatory organization [30]. These efforts can determine the quality of healthcare services in the hospitals.Conclusion
Patient’s care and nursery play important roles for patient treatments and recovery. High quality nursery work is much needed.To read more about this article....Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/abeb/fulltext/nursery-service-in-modern-days.ID.000515.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
Iris Publishers-Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology | Antibacterial Activity of Leptadenia Hastata Leaves Extracts against Some Gastro-Intestinal Isolates
Authored by Muhammad Ali
Abstract
At present, drug discovery research is mainly focused on plant resources and their compounds. The study was conducted to determine the phytochemical composition and antibacterial property of Leptadenia hastata leaf extracts against some gastro-intestinal isolates. Clinical isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Shigella dysenteriae isolated from patients diagnosed with gastro-intestinal disorder were obtained from Microbiology laboratory of Murtala Mohammed Specialists Hospital Kano. Aqueous and ethanol extracts of Leptadenia hastata were prepared separately and subjected for phytochemical screening and antibacterial activity. The antibacterial activity of the extracts was determined using the agar well diffusion. The result indicated the presence of alkaloid, saponin, phenol, flavonoids, glycoside, tannin, steroid and terpenoid in both aqueous and ethanol extracts. The results of antibacterial activity of Leptadenia hastata leaf extracts indicated that extracts possessed antibacterial activity with variable degree of sensitivity against isolates with ethanol extract having higher activity (12.56 mm) than aqueous extract which has an average zone of inhibition of 11.22 mm. statistical analysis of the results showed that S. aureus is the most sensitive isolate. However, there are no statistical significant differences on the sensitivity of the isolates at p<0.05. It is concluded that the extracts of L. hastata possessed antibacterial agents.Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Bacteria; Leptadenia hastata; Gastro-intestinal disorder
Introduction
Natural products have been used over the years as curative agents against many infections and have been exploited in the traditional medicine with their curative potentials well documented [1]. Natural products are defined as natural sources-derived substances having biological activities. These natural products have long been implemented as alternative health care treatment and in the discovery of modern drugs [2]. A major focus of natural product in chemistry has been toward drug design and discovery. However, obtaining scientific proof for the biological activity of natural plants is still challenging [3]. At present, drug discovery research is mainly focused on natural plant resources and their compounds. Most of the currently available therapeutically active drugs are discovered based on the knowledge available from various traditional practices for disease treatments [4].Leptadenia hastata (Pers.) Decne is a perennial plant of the family of Asclepediaceae, the plant is edible non-domesticated vegetable and it is collected in wild throughout Africa. It is one of the important medicinal herbs used in Africa by the traditional healers for treatment of disease and ailment and for food by the local people in terms of hunger due to its high content of valuable nutrients rich in various types of amino acids, fatty acids, terpenes, carotenes, luteines and poly-oxy pregnane [5]. The plant is commonly used in the Northern Nigeria as spices and sauces [6]. Local healers also use the plant for hypertension, catarrh and skin diseases [7]. In certain areas of West Africa, breeders claimed the antifertility effect of their animals after consumption of the leaf and stems of Leptadenia hastata [1]. The main phytochemical constituents of the plant are carbohydrates, steroids, glycosides, flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic compounds [8]. A phytochemical screening conducted by Bello, et al. [9] on Leptadenia hastata leaves extract indicate the presence of phenolic glycosides, tannins, flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, alkaloids and saponins.
Aliero and Wara [10] studied the antibacterial activity Leptadenia hastata leaves extract against Bacillus sp, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella paratyphi and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. They observed clear zones of inhibition after the incubation period. In a study conducted to evaluate the in vitro antibacterial potentials of Leptadenia hastata extracts, the result showed that extracts exhibited antibacterial activities against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 and clinical strain of Staphylococcus aureus), and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and clinical strains Salmonella typhi, Klebsiella pneumoniae) bacteria [11]. The activity of the plant may be as a result of the presence of; alkaloids, saponins, phenolic glycosides, tannins, flavonoids, proanthocyanidins and triterpenes [12]. In many African countries, the plant is used as medicine due to its nutritive and therapeutic properties for the treatment of wounds and stomach upset conditions in children [10]. In view of this, the study was conducted to determine the phytochemical composition and antibacterial property of Leptadenia hastata leaf extracts against some gastrointestinal isolates.
Materials and Methods
Ethical approval
Ethical clearance (MOH/off/797/T.I/49) for the study was obtained from Kano State Ministry of Health through Health Service Management Board Kano with the consent of Murtala Muhammad Specialist Hospital Kano ethical committeeStudy Area
Clinical isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Shigella dysenteriae isolated from patients diagnosed with gastro-intestinal disorder were obtained from Microbiology laboratory of Murtala Mohammed Specialists Hospital Kano. Characterization of the isolates and determination of antimicrobial activity of the extracts against the isolates was conducted in the Departments of Microbiology of Kano University of Science and Technology Wudil. Phytochemical screening of the extract was done at Biochemistry laboratory of Bayero University, Kano.Characterization of the isolates
The isolates were characterized by conventional microbiological methods: Gram staining, Biochemical test (indole, methyl-red, voges proskauer and citrate utilization), motility and lactose fermentation test. Gram staining was done according to the methods described by Cheesbrough [13]. Biochemical tests were done according to the method described by Holt et al. [14]. Lactose fermentation test was done by inoculating the isolates onto the surface of MacConkey agar and incubated at 370 C for 24 hours [14].Identification of plant materials
Letadenia hastata leaves were used in this study. The plant material was obtained at about 7:30 am on 23rd October, 2017 at Mariri village in Kumbotso Local Government Area of Kano State. Identification and authentication of the plant material was done at Herbarium in the Department of Plant Science, Bayero University Kano with the following voucher number BUKHAN 248 and voucher specimen were deposited there for reference.Preparation of extracts
Aqueous and ethanol extracts of Leptadenia hastata were prepared separately. The fresh leaves were washed and air dried for two weeks. After drying, the leaves were grounded to fine powder using sterile pestle and mortar under laboratory condition. Fifty grams (50g) powder of the plant material was soaked in 500 ml each of distilled water and ethanol respectively. The flasks were kept at room temperature for 3 days with intermittent shaking after which filtration was done using Whatman filter paper. The ethanol extracts was evaporated at 60°C using rotary evaporator while the aqueous extract was evaporated at 70°C in water bath until dried extract samples were obtained. All the dried extract samples were dissolved in 30% DMSO separately to the final concentration of 200 mg/mL as a stock concentration. Various concentrations of 100, 75, 50 and 25 mg/mL were made from the stock concentration. The extract solutions were stored at 4°C before use [15].Qualitative phytochemical screening
The screening of the phytochemical constituents of the plant materials for various phytochemical constituents such as terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, reducing sugars, steroid, glycoside, phenol, Anthraquinones, saponin and tannin was conducted using standard methods as described by Sofowora [16] and Trease and Evans [17].Antibacterial activity of the extracts
The antibacterial activity of the extracts was determined using the agar well diffusion [18]. The prepared bacterial suspension equivalent to 0.5 McFarland Standard (1.5 x 106 CFU) was inoculated onto sterile surface of Mueller- Hinton agar medium (MHA) in a Petri-dish. A cork borer of 6 mm diameter size was utilized to produce 5 holes at equidistance on the medium. The holes were supplied with approximately 0.1mL of the prepared extracts at a various concentration of 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg/mL respectively. The plates were allowed to diffuse on the laboratory bench for 1 hour. The inoculated plates were incubated at 370 C for 24 hours. Zones of inhibition produced by the extracts against the test isolates were observed and measured. The experiment was conducted in triplicate and the average values were recorded. Amoxicillin 50 mg/mL (Micro Lab limited) was used as positive control in the experiment.Evaluation of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Broth dilution technique was employed to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration MIC of the extracts. Double fold dilutions were prepared by adding 2mL of 100mg/mL of the extract into a test tube containing 2mL of Nutrient broth, thus producing solution containing 50mg/mL of the extract. The process continues serially up to test tube No. 5, hence producing the following concentrations; 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25 and 3.125 mg/mL respectively. Test tube Number 6 does not contain extracts and serve as negative control. Exactly 0.5 mL of 0.5 McFarland equivalent standards of test organisms were introduced into the test tubes and incubated at 370 C for 24 hours. After incubation the test tubes were observed for growth by checking for turbidity [18].Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
From each tube that did not show visible growth in the MIC, Briefly, 0.1 mL bacterial culture was pipette from MIC tubes which did not show any growth and sub cultured onto the surface of Mueller Hilton agar plates. The inoculated plates were incubated at 370 C for the period of 24 hours. The MBC was recorded as the lowest concentration of extract without single colony of bacteria on Mueller Hilton agar plates [18].Statistical Analysis
The data obtained on antibacterial activity of the extracts against the test isolates was analyzed using One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All the data were computed as means ± standard deviation using statistical program SPSS 21.0 (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences). Probability value of 0.05 was set to determine significant differences level on the activity of the extracts against the tested isolates.Results
Phytochemical screeningThe phytochemical constituents of Leptadenia hastata leaf extract is presented in Table 1. The result indicated the presence of alkaloid, saponin, phenol, flavonoids, glycoside, tannin, steroid and terpenoid in both aqueous and ethanol extracts (Table 1).
Table 1: Phytochemical constituents of Leptadenia hastata leaf extract.
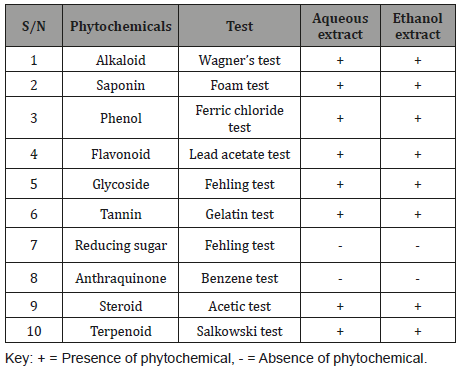
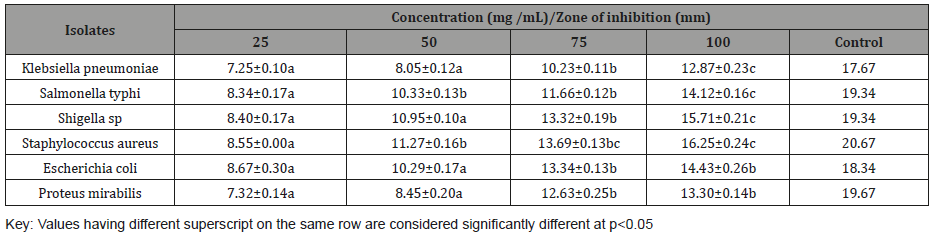
Table 2: Antibacterial activity of L hastata aqueous extract.
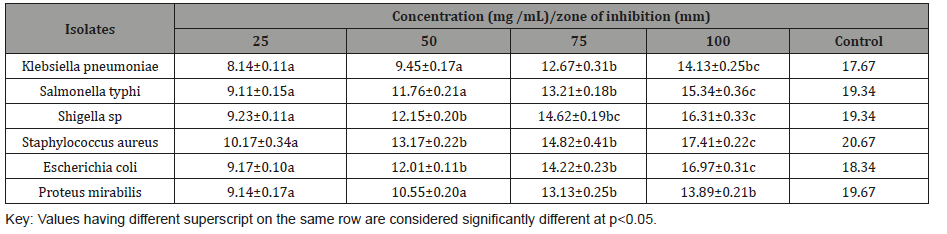
Antibacterial activity of ethanol extract
The antibacterial activity of ethanol extract of L. hastata is presented in Table 3. The results showed that zones of inhibition recorded by the isolates depend on the type of bacterial isolates and concentration of the extracts. Highest zone of inhibition was demonstrated by S. aureus (17.41 mm) at 100 mg /mL. The zone of inhibition of the control (Amoxicillin 50 mg/mL) ranges from to 17.67 – 20.67 mm (Table 3).
Table 3: Antibacterial activity of L hastata ethanol extract.
MIC and MBC of aqueous and ethanol extracts
Minimum inhibitory concentration of aqueous and ethanol extract of L hastata is represented in table below Table 4. The result showed dilutions of various concentrations of aqueous and ethanol extracts of the plant can inhibit the growth and kill the isolates. Lower MIC (3.125 mg/mL) was shown by ethanol extract than aqueous extract. MBC of the extracts ranges between 12.5-50mg/ mL (Table 4).
To read more about this article...Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/abeb/fulltext/antibacterial-activity-of-leptadenia-hastata-leaves-extracts-against-some-gastro-intestinal-isolates.ID.000514.php

Antibacterial activity of aqueous extract
The antibacterial activity of aqueous extract of L. hastata leaf is presented in Table 2 below. The results showed that zones of inhibition recorded by the isolates depend on the type of bacterial isolates and concentration of the extracts. Highest zone of inhibition was demonstrated by S. aureus (16.25 mm) at 100 mg /mL. The zone of inhibition of the control (Amoxicillin 50 mg/mL) ranges from to 17.67 – 20.67 mm (Table 2).Table 2: Antibacterial activity of L hastata aqueous extract.

Antibacterial activity of ethanol extract
The antibacterial activity of ethanol extract of L. hastata is presented in Table 3. The results showed that zones of inhibition recorded by the isolates depend on the type of bacterial isolates and concentration of the extracts. Highest zone of inhibition was demonstrated by S. aureus (17.41 mm) at 100 mg /mL. The zone of inhibition of the control (Amoxicillin 50 mg/mL) ranges from to 17.67 – 20.67 mm (Table 3).
Table 3: Antibacterial activity of L hastata ethanol extract.

MIC and MBC of aqueous and ethanol extracts
Minimum inhibitory concentration of aqueous and ethanol extract of L hastata is represented in table below Table 4. The result showed dilutions of various concentrations of aqueous and ethanol extracts of the plant can inhibit the growth and kill the isolates. Lower MIC (3.125 mg/mL) was shown by ethanol extract than aqueous extract. MBC of the extracts ranges between 12.5-50mg/ mL (Table 4).
To read more about this article...Open access journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/abeb/fulltext/antibacterial-activity-of-leptadenia-hastata-leaves-extracts-against-some-gastro-intestinal-isolates.ID.000514.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
Tuesday, November 26, 2019
Iris Publishers- Open access Journal of Scientific Journal of Research & Reviews| Creating Dynamic Practices: NJCU’s Programs for Student Success
Authored by Jessica Accurso-Salguero
Abstract
This paper will provide an overview of New Jersey City University’s (NJCU) retention initiative programs for low-income, firstyear minority students. The programs provide students with advising, peer-mentoring, college transition workshops, outreach campaigns targeting at-risk student groups, and financial assistance. NJCU’s intrusive advising, serves as a catalyst for connecting students to resources on campus. This paper provides information on the implementation of successful programs and newer programs of promise, such as the Orientation to College and Peer Advisor Liaisons programs. NJCU’s ASCEND Summer Bridge Program, which was developed to assist students who were at a disadvantage academically in entering a four-year college and provides academic preparation, holistic support, advisement, mentoring, orientation to college for first time, full-time freshmen support, and campus engagement. The work conducted at NJCU successfully provides for the needs of students now and in the future.Introduction
Approximately one-third of all college students in the United States are low-income, first-year students [1]. Studies show that low-income, first-year students frequently underperform in secondary school and consequently college [2]. A significant percentage of these college students are unprepared for collegelevel work in at least one of the following areas: reading, writing, or mathematics [3]. Research indicates that college bound students with weak academic skills are often required to complete at least two semesters of developmental coursework before enrolling fulltime solely in college-level courses [4,5]. Over the past five years, at NJCU, approximately 87% of students needed to enroll in at least one developmental English or Math course, and 69% of these students needed to enroll in two developmental courses in English and Mathematics. With this in mind, it is imperative to understand that student enrollment, retention, and graduation depend on access and the level of institutional support provided [6].Low-income, first-year students who engage in heightened interactions with individuals on campus as well as have access to academic, cultural, social, and personal means to engage with teachers and peers increases their academic success and retention in college [2]. NJCU has begun (within the last 5 years) and contributes to its largely low-income, first-year students by providing mentorship, college transition workshops, outreach campaigns targeting at-risk student groups, and emergency financial assistance. Through campus-wide data-driven processes, NJCU has made a commitment to student success as one of its highest institutional priorities as evidenced in the 2013-2018 Strategic Plan [7]. NJCU’s commitment is supported in the development of several programs, many that serve first-time, full-time freshmen who have been placed in at least one developmental course.
Additionally, NJCU’s programs support the general student population who work part-time or full-time, live off-campus, and support families; a common characteristic of first-time, full-time students [8,9]. The intention of NJCU is to support low-income, firstyear students who experience limited opportunities for academic success. The following paper presents a brief history of NJCU, the types of programs that are available to NJCU students, specifically programs related to advisement and Summer Bridge, and future intentions to further the NJCU mission and create student success for all students.
New Jersey City University Background
The history of NJCU dates back to 1929 when it was first named New Jersey State Normal School at Jersey City. The school was later renamed the New Jersey State Teachers College at Jersey City in 1935 and Jersey City State College in 1958 before assuming its current role and name in 1998 when it was approved for university status. At that time, The College of Arts and Sciences, The College of Education, and The College of Professional Studies were established and in 2002, NJCU and Brookdale Community College located in Wall, NJ, initiated a “Communiversity” partnership which offered bachelor and master’s degree completion programs for residents in central and southern New Jersey. Later, in 2007, NJCU opened a facility for graduate business programs in Jersey City’s waterfront financial district and in 2015, the NJCU School of Business opened.Currently, NJCU enrolls 8,500 students, of which 6,600 are undergraduates. NJCU host 4 colleges, offers 43 undergraduate and 30 graduate degrees, and is both a Hispanic Serving Institution (HIS) and a Minority Serving Institution (MSI). The demographics of NJCU are made up of a student body that is 35% Hispanic, 21% African American, 23% White, and 8% Asian, and as many as 95% of students are commuters. The average household income is $42,000, and Pell eligible students stand at 84% overall. To date, NJCU engages in significant institutional wide investments in student success, has invested $1.5 million in institutional financial aid and scholarships, $500k in student focused programming, $400k in improved systems and technology, supported 10 new fulltime administrative positions, and has staff that spends countless hours in meetings and serving on committees.
Programs Offered
An effective strategy in influencing undergraduate retention and academic achievement has been through increasing student interactions with faculty, staff, advisors, peers, and administrators [10]. Additionally, recent retention research stresses crossdepartmental institutional responsibility for retention through a wide-range of programs [11]. NJCU institutes numerous outreach programs and campaigns and takes a holistic approach to undergraduate retention, which includes all members of the campus. Furthermore, NJCU promotes retention and student success through offering financial literacy workshops, pairing students with one financial aid counselor, using peer to peer mentorship, increasing faculty participation, promoting academic advisor targeted outreach, creating socially engaging activities, bridging the curricular and extra-curricular, and offering supplemental instruction and tutoring. NJCU’s focus on meeting students where they are has allowed for an inclusive campus climate bolstered by peer mentoring, an institution of student support through financial assistance and awareness, university advisement, and the Summer Bridge Program.Campus Climate
The lack of diversity in a student body, faculty, and institutional leadership negatively affects the undergraduate retention of minority students [5]. For underrepresented students, it is important to remove cultural barriers so that students can connect to the larger campus community [12]. Social support networks and student organizations play an important role in helping students feel they belong within an institution [6]. Positive interactions between students and faculty were identified as a major reason contributing to the retention of students [5]. When Latino, Black, and other minority students perceive their campuses as being ethnically diverse they are much more likely to be retained. Conversely, minority students who reported more discrimination or acts of racial bigotry on campus had lower academic performance, are less satisfied with their academic and intellectual development, and have less commitment to the institution or their own academic achievement [5], indirectly impacting the student’s decision to persist. However, in a campus environment that actively encourages tolerance and acceptance and appropriately engages students in academic and social discourse, students develop a sense they belong and are accepted [5].Students who participate in community service activities, religious clubs, student government, sports teams, tutoring programs, and interact with peers and faculty outside of the classroom, were found to have higher sense of belonging [12]. Interactions students have with individuals on campus can influence a students’ sense of connectedness to the institution, as well as their ability to navigate the campus culture, and succeed academically. Therefore, offering accessible academic, personal, and social support services on campus is a key approach to improving undergraduate retention. Programs and initiatives designed to support undergraduate retention address both formal and informal student experiences inside and outside of the classroom and at NJCU the focus on welcoming diversity and including all students regardless of religion, skin color, ethnicity, sexual identity, or any other characteristic creates a climate of acceptance.
Peer Mentoring
Peer mentoring is one of the most effective methods to increase student retention, graduation rates, and cross-cultural understanding of undergraduate students [13]. The goal of NJCU’s peer mentoring efforts is to foster academic success and enhance the psychosocial functioning of new students as they transition from high school to a college environment. Peer mentoring was first offered in the fall of 2015 to all minority first-time freshmen during the first week of the academic year, and participation was voluntary.The first cohort of peer mentors were selected from a pool of minority candidates who were in their sophomore year or beyond, had a cumulative grade point average of 3.0 or better, and who were involved in at least one student organization or club.
Today, and to successfully engage in peer mentoring, candidates are interviewed by a coordinator and selected based on their commitment to the institution and their knowledge of how to navigate the campus, both socially and administratively. Peer mentors are assigned a caseload of twenty mentees and are paid a stipend for the semester in which they mentor. Incoming students and families begin meeting mentors from November and beyond at which time NJCU’s financial workshops begin. NJCU’s Peer Mentoring Program requires students to meet with their mentees three to four times a semester and to check-in with their mentees through phone calls or email throughout the academic year. The list of topics that peer mentors use in meetings with a mentee include reviewing academic support services that are available, introducing mentees to student activities and organizations, and ensuring mentees are not experiencing academic or social issues adjusting to college. Peer mentors also promote university resources, field questions, and support students transitioning to college. Incoming students are introduced to campus life, tutoring services, the health and wellness center, the counseling center, the student government and various clubs. Peer Mentors meet with their students individually and in groups during the summer as well as throughout the academic school year. Peer Mentorship, coupled with intentional family programs, and culturally relevant activities in and outside of the classroom are essential in creating a healthy campus climate for our students.
Financial Assistance and Awareness
It has been well established that working while attending college, paying for tuition through loans or grants, and having financial need are factors that affect undergraduate retention [14]. Typically, if there exists a gap in financial support, even after institutional and family contributions, students tend to register part-time, work longer hours, or live off-campus, all of which have a negative impact on retention [12]. Financial aid and support matters to all students, especially Latino, Black, and other minority students as low-income minority students who receive financial aid are more likely to persist than their counterparts who did not receive financial aid [9]. These findings were particularly revealing in studies involving first-year Latino and Black students. For this student population, the decision to attend or persist in college directly relates to several factors, among them understanding how to complete a FAFSA.In the 2016-2017 school year, fall to spring first time, full-time retention was at 37% due to 90% of the students not completing their FAFSAs, the majority of these students being Latino and Black. To support students in need, NJCU instituted a program in which the College was able to offer financial aid, financial literacy, and academic skills workshops monthly during the academic year. Professional staff members from enrollment management and student affairs conducted the workshops, and attending the workshops was voluntary and made available to all first-time freshmen students. Evidence of these initiatives was apparent in that last year’s cohort persisted by more than 87% and registered for the spring semester because their FAFSA’s were complete.
Furthermore, in reviewing and reaching out to first-time freshmen who have an outstanding tuition balance, we found that many had unmet financial need, even after receiving federal and state aid and loans. For the students who were unable to cover the cost of tuition and books out of pocket, the University allocated individual emergency grants of up to $2,000 to cover an outstanding tuition balance. A financial aid committee, based on a review of a student’s financial aid profile and any proof of extenuating circumstances a student or their family could provide, and award these additional grants. In the first year of implementation, twenty-one grants were awarded, with the average award being approximately $500. For first-time freshmen who had administrative holds on their records, ranging from immunizations, financial aid issues, and outstanding balances, financial literacy, and aid options were addressed student by student through the support of one-on-one sessions with assigned financial aid advisors. Financial support programs and initiatives only make up part of the work being conducted at NJCU to offer support to all students, and especially low-income, firstyear students.
University Advisement
NJCU’s Advisement Center serves as a catalyst for connecting students to resources on campus. An additional resource for incoming freshmen, NJCU implemented intrusive advising in the fall of 2016. The priorities of intrusive advising are a focus on retention and graduation, academic support, intensified academic advisement, accountability, supervision, and consistency. To date, we have connected more than 75% of our students to advising sessions, and 50% to our tutorial services, as well as workshops hosted by our advisors. These interventions have increased retention by 65% in good standing for full-time freshmen. Staff members or peer mentors, depending on the issue, reach out through email, text, or by phone to connect with students to assist in resolving an issue or to provide any assistance needed. Furthermore, NJCU’s advisors have now started teaching Orientation to College (OTC) courses, tracking students by cohort, holding personalized advisement sessions, and creating relationships with students by “meeting them where they are”. By creating a dynamic intrusive advisement program at NJCU, an atmosphere geared toward student success is created. Along with the success of advisement at NJCU, the Summer Bridge Program has been instrumental in serving low-income, firstyear students.Summer Bridge Program
During the winter of 2014, the President of NJCU hosted a university wide retreat focused on student success. During this retreat, the University identified the need for cross-divisional efforts to improve student success and that the needs of minority students, especially Latinos, are uniquely different. In 2015, NJCU created Achieving Success by Cultivating Excellence and Nurturing Discovery (ASCEND). A significant percentage of college students are unprepared for college-level work in reading, writing, or mathematics and Summer Bridge programs help mitigate these occurrences [5,15].The student demographics for NJCU’s ASCEND Program students are as follows: 100% of these students apply for federal aid, 100% are part of underrepresented minorities, 80% have some level of unmet need, 76% come from household incomes of less than $60,000, and approximately 90% are PELL eligible and require developmental support. The ASCEND intensive sevenweek academic preparation and college orientation program was designed to help students advance at least one level by taking developmental summer courses. Expediting the timeframe when students enroll in full semesters of college-level courses after high school increases the likelihood that students complete. Each summer, approximately 100 students participate in the ASCEND Summer Bridge Program at NJCU and bridge the “summer learning gap” in an innovative way that helps students’ develop and integrate their academic, physical, social, and emotional well-being as well as environmental awareness and stewardship principles.
Although the ASCEND Summer Bridge Program started slowly and the first year’s 2015 retention rate from fall to fall was 41%, the success of the program grew and the second year had a success rate of 44%, followed by a third year (2017) success rate of 69%. Summer 2017, 100 students successfully completed the program, 43 students tested out of developmental math, and 10 students increased their scores by at least 10 points. At the conclusion of the program in 2017, more than half of the students tested out of developmental classes and the enrollment overview in Table 1 below supports these numbers (Table 1). The ASCEND Summer Bridge Program’s primary components are academic preparation, academic support, academic advising, peer mentoring, orientation to college for first time, full-time freshmen, and campus engagement activities. The Program promotes peer mentorship, daily workshops that promote self-efficacy, relationship with faculty, intramural sports, and individual and group guidance counseling. Peer mentors successfully facilitate tutoring, social engagement with clubs and organizations on campus, assist with financial aid, advisement, and registration. Additional goals of the NJCU ASCEND Summer Bridge Program are to develop and strengthen students’ connections with advisors, faculty, and staff to provide students with knowledge critical to success in college (e.g. study skills, time management, and campus life), and enhance students’ sense of belonging. Additionally, advisors teach Orientation to College courses, track students by cohort, hold personalized advisement sessions, and create relationships with students by meeting them where they are. Advisors focus on giving students an opportunity to build relationships with students, facilitate workshops, engage in personalized one on ones, and track and assist students throughout the academic school year. Given the significant challenges inherent to any Summer Bridge Program, ASCEND has created a positive first-year experience for NJCU students.
Methodology and Results
Using a mix of methods, such as regression analysis, cohort tracking, predictive analytics, focus groups, T-tests, and Chi-Square analysis, NJCU has been able to effectively track the success of its programs as outlined in Table 2 and Figure 1 below. Through the various initiatives outlined above, NJCU has been able to not only increase the first-year retention rate but has also helped at-risk, remedial, and special cohort students persist (Table 2) (Figure 1).
Looking Toward the Future
As reiterated throughout this study, many low-income, firstyear students at NJCU are not prepared for college-level work. First-year performance often determines whether students decide to continue, and poor academic self-efficacy and self-doubt lead to drop out. At NJCU, outcome metrics include enrollment trends, pretest and post-test assessments, fall placement, student engagement, fall-to-fall retention rate, first term GPAs, first year cumulative GPAs, first year degree credit accumulation, and graduation rates. From these findings, NJCU continues to implement new programs, such as the Integration of Advisement, Block Scheduling, Orientation to College (OTC) and Peer Advisor Liaisons (PALs) programs and is experiencing significant success. Each member of the NJCU community is personally dedicated to and accountable for ensuring all students receive a high-quality education and a first-rate experience that leads to timely graduation with minimal debt, an academically rich degree, and a meaningful future upon graduation. With the unique approach of including the family members of students through culturally relevant outreach, including office staff (in some cases) with at least five Spanish-speaking individuals, and the ability to share a common culture, NJCU is on the cutting edge of student retention and success in a culturally diverse area. NJCU’s dedication to student success, a reflection of a 2013-2018 Strategic Plan [7] is a reality and a guidepost for other colleges and universities serving low-income, first-year students.
To read more about this article.... Open access Journal of Scientific Journal of Research & Reviews
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/sjrr/fulltext/creating-dynamic-practices-njcus-programs-for-student-success.ID.000516.php
o know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
Iris Publishers- Open access Journal of Scientific Journal of Research & Reviews | Recognising Acute Lamotrigine Induced Tourette’s Syndrome in Adults
Authored by Angus-Leppan H
Abstract
We report a woman with epilepsy developing acute reversible lamotrigine induced Tourette’s syndrome. This rare reaction is important as lamotrigine is used widely in neurology, psychiatry and pain management.Case Report
After six years of remission on carbamazepine, a 33-yearold woman with focal epilepsy of unknown cause had a seizure three weeks post-partum. Within 48 hours of starting lamotrigine (25mg twice daily), she developed severe complex motor tics and coprolalia. There was no personal or family history of tics or obsessionality. Tourette’s resolved within 72 hours of stopping lamotrigine. She declined re-challenge. There is no recurrence over nine years. Previous reports of Tourette’s in patients treated with lamotrigine for epilepsy, bipolar disorders or refractory depression demonstrated a dose-dependent effect (Table). Our patient’s symptoms occurred and resolved within 48 hours (compared to a mean 5 months and 72 hours respectively in all reports, see Table), more rapidly than previously reported. The severity of lamotrigine-induced Tourette’s varies from mild to severe. In most patients, lamotrigine was withdrawn, but in 5/16 dose reduction resolved symptoms (Table). Several cases recurred on re-challenge, and 7/16 occurred in adults (see Table) in contrast to primary Tourette’s syndrome (commencing at mean 7 years), occurring in 0.5% of the population [1].Carbamazepine, phenobarbital and phenytoin [2] as well as lamotrigine, are rare secondary causes of Tourette’s. Only one previously reported patient had a prior tic disorder and 2/16 had pre-existing obsessional traits (Table). No predisposing or genetic factors have been identified, in contrast to primary Tourette’s syndrome [1].
Tourettes syndrome is postulated to be due to basal ganglia and frontal dysfunction [3], along with genetic factors [1]. The mechanism of the reaction to lamotrigine is uncertain. Inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels and subsequent attenuation of pre-synaptic glutamate release modulates basal ganglia circuitry and is postulated as the cause [3]. Lamotrigine-mediated nicotinic receptor agonism, mediating basal ganglia dopamine release, has also been suggested [3]. Neither hypothesis explains susceptibility in such a small percentage of patients.
In our secondary care cohort, lamotrigine induced Tourettes occurred in 0.3% of adults with epilepsy, and a previous report estimated 1.3% in children [4]. The reaction can be delayed up to 10 months after commencing Lamotrigine. A careful drug history is important in Tourette’s syndrome, especially if atypical features, such as adulthood onset, or absent family history. Clinicians should be aware of this reversible cause of Tourette’s syndrome.
Acknowledgement
Our thanks to the patient who gave informed consent for this publication.
To read more about this article... Open access Journal of Scientific Journal of Research & Reviews
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/sjrr/fulltext/recognising-acute-lamotrigine-induced-tourettes-syndrome-in-adults.ID.000515.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
Monday, November 25, 2019
Iris Publishers-Open access journal of Online Journal of Cardiovascular Research | Endovascular Debulking in Therapy of Occluded Lower Limb Bypass
Authored by Miroslav Bulvas
Mini Review
The goal of surgical and/or endovascular therapy in patients with lower limb ischemia is the elimination of return or progression of serious and threatening ischemic symptoms (rest pain, ischemic ulcers or gangrene) [1-3]. Thus, bypass occlusion can be associated with renewed acute or critical ischemia and endangered lower extremity. Early (> 30 days) graft failure rate 6.3% was reported in the study that collected 9217 bypass procedures [4] with higher frequency in preceding emergency and re-operative procedures (8.2%). Typically, it can be ascribed to technical factors (kinking or twisting of the graft, technical anastomotic problems. inadequate runoff, clamp injury, retained valves,) and prothrombotic state [5]. Intermediate graft failure (from 30 days to 18 months) is commonly associated with my intimal hyperplasia formation at the sites of anastomoses or valves (venous bypass grafts). Late graft failure is largely caused by the progression of atherosclerosis in the outflow or inflow vessels Figures 1 & 6. Excellent and long-lasting results (5-year primary patency rate 85-88%) can be expected with aortoiliac reconstruction at low risk patients. Acute thrombosis of an aortofemoral graft limb occurs in about 2% of patients during early perioperative period [6]. Primary patency rates 87-100% (1 month), 69-86% (1 year) and 51-72% (5 years) were reported [7] in femoropopliteal bypasses with better results for suprageniculate and autovenous saphenous grafts.
Patients who have undergone placement of lower limb bypass grafts are followed up with periodic evaluations that record return or progression of ischemic symptoms. Therefore, hemodynamic deterioration caused by progression of proximal or distal atherosclerosis and/or intimal hyperplasia can be detected before thrombosis and occlusion develop. In those cases, preventive balloon angioplasty, stenting or percutaneous atherectomy are used to assist the primary patency.
Surgical treatment of acutely thrombosed vein graft is usually associated with thrombectomy, thrombolysis and subsequent repair of the defects responsible for graft failure. Unfortunately, only 23% of vein grafts remained patent 3 years after successful thrombolysis and revision [5,8]. For intermediate to late vein graft failure, a new surgical reconstruction is recommended in patients with threatened extremity. Nevertheless, advanced comorbidities and anatomy can preclude major reoperation. Furthermore, it can be difficult to find sufficient vein for reoperation in patients with occluded prosthetic grafts. For secondary bypass grafts, 25% primary patency (prosthetic) and 43% (autogenous vein) were reported [5] five years after reoperation.
Surgical or thrombolytic limitation is the driving force for usage of the modalities with purely endovascular, mechanical approach in the management of occluded bypasses. For the Rotarex catheter, 98 -100 % technical success was reported in the series with acute and subacute occlusions of femorpopliteal bypasses [9,10]. Lichtenberg et al. managed 22 patients with venous (12) and prosthetic (10) occluded by passes without major complication, death or reintervention during 6-month follow-up. Wissgott et al. reported 98 % technical success in 42 patients with 81% of venous bypasses, 4.8% of complications (no amputation, no death) and 66% of 12-month primary patency [11]. Reported lower primary success (78%) in 9 patients with occluded femoropopliteal bypasses compared to 91 cases of infraaortic occlusions. Mixed series of 316 patients [12] with acute and subacute lower limb ischemia (72 femoropopliteal bypass occlusions) reached 100% technical success at the level of target vessels with only a minor complication (8%) associated with debulking therapy. The overall therapeutic success was negatively influenced by infrapopliteal artery status and the low potential for effective endovascular and surgical treatment in this runoff area [12].
Conclusion
Mechanical debulking with the Rotarex catheter can be used as an initial treatment in patients with occluded lower limb bypasses especially in those, at high surgical risk or predisposed to bleeding.
To read more about this article...Open access journal of Online Journal of Cardiovascular Research
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/ojcr/fulltext/endovascular-debulking-in-therapy-of-occluded-lower-limb-bypass.ID.000530.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
Iris Publishers-Open access journal of Online Journal of Cardiovascular Research | In There any Connection between Normal Blood Pressure and Watching Cricket?
Authored by Arslan Hassan
Abstract
The objective of our current study was to correlate interest in watching cricket and blood pressure. Blood pressure applies force on blood to move through our body and transport oxygen or nutrients to our tissues. The sphygmomanometer is a device that measure the pressure of blood on our arteries. It is measured in mmHg unit. It is measured in two figures – systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Cricket is a game which is famous worldwide. There is great difference in interests of people according to their thinking. Some people consider cricket a noble game and take interest in watching and playing. There are also people who do not like cricket and consider it a time wasting on even playing. There is also difference among people which are more interested and extremist for cricket. It is concluded from the current study that there is no scientific relationship between normal blood pressure and watching cricket [1].Keywords:Blood pressure; Sphygmomanometer; Systolic and diastolic; Watching cricket
Introduction
Normal blood pressure is necessary for living of an individual. The pressure of blood applies force on blood to move through our body and transport oxygen or nutrients to our tissues. It is also important that it transport WBCs and antibodies and hormones to create the immunity of our body. Blood pressure may increase to much or decrease to very low both are dangerous situations for our body. The sphygmomanometer is a device that measure the pressure of blood on our arteries and consist of cuff, hand pump and electric meter [2]. Blood pressure always measure in unit of mmHg (millimeters of mercury). Blood pressure always measure in two figures – first value is high due to heart’s contraction called systolic pressure and second is low value due to resting period of our heartbeats called diastolic pressure [3]. For example, normal blood pressure of adults is 120mmHg and 80mmHg, systolic is higher than diastolic pressure. If blood pressure increases it increases the chances of hearts diseases and hypertension [4,5], failure of kidney and can cause the problems of eyes. It is related with age which may harden the blood arteries, so pressure is increased. If the blood pressure is very low to 80/50 then it will make you weak, lightheaded, and dim. The causes of low blood pressure may be dehydration (not drinking sufficient water), much loss of blood, or taking too much medicines. To maintain normal blood pressure is very necessary for our life so we must take some steps in our daily life routine to make blood pressure normal, always try to retain the fit weightiness, take exercise daily, eat well food, smoking and alcohol keep far away from body and try to manage tension. Higher blood pressure can cause the serious diseases and very dangerous for health so always try to maintain the normal blood pressure [6].Cricket is a game which is famous worldwide and about 2.5 billion fans of cricket specially in Asia, Australia and UK. Cricket is played between two teams both have 11 players. There are three formats of cricket internationally T20, ODI and Test. There is great difference in interests of people according to their thinking. Some people consider cricket a noble game and take interest in watching and playing. There are also people who do not like cricket and consider it a time wasting on even playing. There is also difference among people which are more interested and extremist for cricket. According to their interest in games, many types of fans come into seeing [7]. Some are quite fans which seems quite from outside but cheering inside for teams. Some are loud fans which are always excited on every type of playing. Some are drunk fans which throw things and become uncontrollable on losing. Some people are allknowing fans which gives analysis before and after match and on every over of playing. Some are temporary fans which may left their teams when they are not playing well. Some are positive fans which love their teams in every situation. So, people have different types of interests about the same sport cricket [8].
The object of current study was to examine the connection between normal blood pressure of people and variation of interest among people for watching cricket [9].
Material and Methods
Protocol to Examine the blood Pressure
Firstly, we consent the subjects to calculate the pressure of blood on arteries. They gave us permission and we measure their blood pressure by sphygmomanometer one by one and inquired from subjects that they take interest in watching cricket or not and listed them by systolic pressure with people’s interest in watching cricket and another list of diastolic pressure with interest of people in cricket [10]. Total of 190 subjects participated in the current study. All the subjects were the students of Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan.Statistical analysis
Statistical Analysis and T-test that were applied on values for result was made by Microsoft Excel.Results and Discussions
Table 1 of systolic blood pressure, we calculated the average of blood pressure of all males and females separately. Then we calculated the standard deviation of all values of blood pressure of males and females and. Then we calculated the p– value in similar way. p– value of 0.05 is considered as standard value. Males which are interested in watching cricket have the average systolic blood pressure of 129 and standard deviation is 14. Females which are interested in watching cricket have average systolic blood pressure is 118 and standard deviation of 13. Both males and females have p value higher than the standard value.Table 2 of diastolic blood pressure, we calculated the average of diastolic blood pressure of males, females and combine. Males those are interested in cricket have average diastolic blood pressure 75 and standard deviation 13. Females those are interested in cricket have average diastolic blood pressure 74 and standard deviation of 11. Males those are not interested in watching cricket have average diastolic blood pressure is 62 with SD of 12 and females with average blood pressure those are not interested in watching cricket is 75 with SD of 13. P – value of males and females is higher than 0.05. So, the relation between the average diastolic blood pressure and people’s interest in watching cricket is non-significant.
Conclusion
It is concluded from the current study that there is no scientific relationship between normal blood pressure and watching cricket.
To read more about this article...Open access journal of Online Journal of Cardiovascular Research
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/ojcr/fulltext/in-there-any-connection-between-normal-blood-pressure-and-watching-cricket.ID.000529.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers
What is the indexing list of Iris Publishers?
ROAD:
https://portal.issn.org/api/sear...[]=MUST=keyproper,keyqualinf,keytitle,notcanc,notinc,notissn,notissnl,unirsrc=irispublishers&search_id=1633309
openarchives:
The Open Archives Initiative develops and promotes interoperability standards that aim to facilitate the efficient dissemination of content. OAI has its roots in the open access and institutional repository movements. Continued support of this work remains a cornerstone of the Open Archives program. Over time, however, the work of OAI has expanded to promote broad access to digital resources for eScholarship, eLearning, and eScience
Scilit :
The name Scilit uses components of the words “scientific” and “literature”. This database of scholarly works is developed and maintained by the open access publisher MDPI.
Scilit is a comprehensive, free database for scientists using a new method to collate data and indexing scientific material. Our crawlers extract the latest data from CrossRef and PubMed on a daily basis. This means that newly published articles are added to Scilit immediately.
DRJI :
DRJI provides ready access to education literature to support the use of educational research and information to improve practice in learning, teaching, educational decision-making, and research. Directory of Research Journals Indexing is a free online service that helps you to find web resources for your articles and research. With millions of resources available on the Internet, it can be difficult to find useful material. We have reviewed and evaluated thousands of resources to help you choose key websites in your subject. Our indexed journals will be submitted to all social networks and world's top most indexing and they will be displayed on world's top electronic library. In short, all journals will reach all continents.
Semantic Scholar :
Semantic Scholar is a project developed at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence. Publicly released in November 2015, it is designed to be an AI-backed search engine for scientific journal articles. The project uses a combination of machine learning, natural language processing, and machine vision to add a layer of semantic analysis to the traditional methods of citation analysis, and to extract relevant figures, entities, and venues from papers. In comparison to Google Scholar and PubMed, Semantic Scholar is designed to highlight the most important and influential papers, and to identify the connections between them.
As of January 2018, following a 2017 project that added biomedical papers and topic summaries, the Semantic Scholar corpus included more than 40 million papers from computer science and biomedicine. In March 2018, Doug Raymond, who developed machine learning initiatives for the Amazon Alexa platform, was hired to lead the Semantic Scholar project. As of August 2019, the number of included papers had grown to more than 173 million after the addition of the Microsoft Academic Graph records
Google Scholar :
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes most peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other scholarly literature, including court opinions and patents. While Google does not publish the size of Google Scholar's database, scientometric researchers estimated it to contain roughly 389 million documents including articles, citations and patents making it the world's largest academic search engine in January 2018. Previously, the size was estimated at 160 million documents as of May 2014.] An earlier statistical estimate published in PLOS ONE using a Mark and recapture method estimated approximately 80–90% coverage of all articles published in English with an estimate of 100 million. This estimate also determined how many documents were freely available on the web.
Cosmos:
Cosmos Foundation was founded by renowned scientists. A group of 100 scientist from various countries in different disciplines are started Cosmos (2010) with specific objective of providing quality information to the researcher. We offer academic database services to researcher. We provide impact factor and index of academic journals, books. We maintain academic database services to researchers, journal editors and publishers. Cosmos provides a detailed report of individual journal for further improvement of respective journal overall look up and technical aspect for better Impact Factor.
Cosmos provides Quantitative and Qualitative tool for ranking, evaluating and categorizing the Journals for academic evaluation and excellence. This Factor is used for evaluating the prestige of Journals. The evaluation is carried out by considering the factors Like Paper Originality, Citation, Editorial Quality, and Regularity & International Presence.
We perform the in-depth analysis method. The acceptance and rejection rates of journals can be a determining factor. Low acceptance rate, high rejection rate journals are considered the best and most prestigious journals, as the acceptance criteria is of high quality standard. Many journals and societies have web pages that give publication data and style requirements and often include acceptance/rejection rates. The paper copy of the journal occasionally includes this data and will always provide current contact information, whether a journal is indexed in the major indexing/abstracting service in the field is another criteria that can be used to assess the worth and quality of a journal.
BASE :
BASE is one of the world's most voluminous search engines especially for academic web resources. BASE provides more than 150 million documents from more than 7,000 sources. You can access the full texts of about 60% of the indexed documents for free (Open Access). BASE is operated by Bielefeld University Library.
We are indexing the metadata of all kinds of academically relevant resources – journals, institutional repositories, digital collections etc. – which provide an OAI interface and use OAI-PMH for providing their contents (see our Golden Rules for Repository Managers).
The index is continuously enhanced by integrating further sources (you can suggest a source which is not indexed yet). We are working on several new features like a claiming service for authors within the ORCID DE project.
BASE is a registered OAI service provider. Database managers can integrate the BASE index into their local infrastructure (e.g. meta search engines, library catalogues). Further on there are several tools and services for users, database and repository managers.
Indexcopernicus :
All journals may be registered in the ICI World of Journals database. The database gathers information on international scientific journals which is divided into sections: general information, contents of individual issues, detailed bibliography (references) for every publication, as well as full texts of publications in the form of attached files (optional). Within the ICI World of Journals database, each editorial office may access, free of charge, the IT system which allows you to manage your journal's passport: updating journal’s information, presenting main fields of activity and sharing the publications with almost 200 thousand users from all over the world. The idea behind the ICI World of Journals database is to create a place where scientific journals from all over the world would undergo verification for ‘predatory journals’ practices by scientific community. The ICI World of Journals database allows journals which care about completeness and topicality of their passports to build their citation rates and international cooperation.
Publons :
Publons is a commercial website that provides a free service for academics to track, verify, and showcase their peer review and editorial contributions for academic journals. It was launched in 2012 and by 2018 more than 500,000 researchers have joined the site, adding more than one million reviews across 25,000 journals. Publons' mission is to "speed up science by harnessing the power of peer review". Publons claims that by turning peer review into a measurable research output, academics can use their review and editorial record as evidence of their standing and influence in their field. Publons says its business model is based on partnering with publishers.
Publons produces a verified record of a person's review and editorial activity for journals. This evidence is showcased on reviewers' online profiles and can be downloaded to include in CVs, funding and job applications, and promotion and performance evaluations.
Publons also provides:
• tools for publishers to find, screen, contact, and motivate peer reviewers;
• data and publications about global peer review behaviour;
• peer review training for early-career researchers; and
• features for academics to discuss and evaluate published research.
Researchbib :
ResearchBib is open access with high standard indexing database for researchers and publishers. Research Bible may freely index journals, research papers, call for papers, research position.
We share a passion to build research communities to discover and promote great research resources from around the world and maximize researchers’ academic social impacts.
Worldcat :
WorldCat is the world's largest network of library content and services. WorldCat libraries are dedicated to providing access to their resources on the Web, where most people start their search for information.
You can search for popular books, music CDs and videos—all of the physical items you're used to getting from libraries. You can also discover many new kinds of digital content, such as downloadable audiobooks. You may also find article citations with links to their full text; authoritative research materials, such as documents and photos of local or historic significance; and digital versions of rare items that aren't available to the public. Because WorldCat libraries serve diverse communities in dozens of countries, resources are available in many languages.
Sciforum:
Sciforum is an event planning platform that supports open science by offering the opportunity to host and participate in academic conferences. It provides an environment for scholarly exchange, discussion of topics of current interest, building of networks and establishing collaborations. Sciforum was launched in 2009 by MDPI, an academic open-access publisher with headquarters in Basel, Switzerland.
Sciforum does not only offer the possibility to participate in conferences, but invites scientists to organize their own conferences. The organizers reduce their administrative efforts thanks to an online tool that supports all aspects of conference organization, including setting up and maintaining the conference website, managing the peer-review process, publishing the conference proceedings, handling and coordinating the conference schedule, registration, billing, sponsors, etc. Organizers can choose between physical and online conferences and whether they require administrative support from Sciforum staff.
Refseek :
RefSeek is a web search engine for students and researchers that aims to make academic information easily accessible to everyone. RefSeek searches more than five billion documents, including web pages, books, encyclopedias, journals, and newspapers.
RefSeek's unique approach offers students comprehensive subject coverage without the information overload of a general search engine—increasing the visibility of academic information and compelling ideas that are often lost in a muddle of sponsored links and commercial results.
JURN’s
JURN’s unique strength is coverage of open access arts and humanities journals, something which has been highly curated and refined over a period of many years. See the JURN Directory for a list of all the English-language arts and humanities titles indexed, although please note that this list does not cover the many journals included in JURN that are published in other languages. In March 2014 JURN became a multidisciplinary index for open access articles, following the completion of a large initial intake of open journals on ecology, nature, palaeontology, business, law, economics and the practical healthcare aspects of biomedical. Also added were several open science full text aggregators, selected full-text university repositories, and all known full-text subject repositories. In early 2015 many armed forces / self-defence journals were added, alongside more titles in business and law. In September 2015 mapping science journals were included, along with many of the more important open geology / geophysics ejournals. By November 2015 the very large intake of eco/nature ejournals had been completed, pushing the total of such English-language journals indexed to over 500. An intake of the smaller geology and geophysics journals is scheduled for late 2016.
Washington State University:
Washington State University (Washington State, WSU or Wazzu) is a public research university in Pullman, Washington. Founded in 1890, WSU is one of the oldest land-grant universities in the American West and features programs in a broad range of academic disciplines. With an undergraduate enrollment of 24,470 and a total enrollment of 29,686, it is the second largest institution of higher education in Washington state behind the University of Washington. The WSU Pullman campus is perched upon a hill, characterized by open spaces, views, deep green conifers, and a restrained red brick and basalt material palette—materials originally found on site. The university is nestled within the rolling topography of the Palouse in rural eastern Washington and remains intimately connected to the town, the region, and the landscape in which it sits.
The university also operates campuses across Washington known as WSU Spokane, WSU Tri-Cities, and WSU Vancouver, all founded in 1989. In 2012, WSU launched an Internet-based Global Campus, which includes its online degree program, WSU Online. In 2015, WSU expanded to a sixth campus, known as WSU Everett. These campuses award primarily bachelor's and master's degrees. Freshmen and sophomores were first admitted to the Vancouver campus in 2006 and to the Tri-Cities campus in 2007. Enrollment for the four campuses and WSU Online exceeds 29,686 students. This includes 1,751 international students.
WSU's athletic teams are called the Cougars and the school colors are crimson and gray. Six men's and nine women's varsity teams compete in NCAA Division I in the Pac-12 Conference. Both men's and women's indoor track teams compete in the Mountain Pacific Sports Federation
Sindexs:
Scientific Indexing Services (SIS) was founded by renowned scientists. A group of 70 scientist from various countries in different disciplines are started SIS with specific objective of providing quality information to the researcher. SIS offering academic database services to researcher. It's mainly: citation indexing, analysis, and maintains citation databases covering thousands of academic journals, books, proceedings and any approved documents SIS maintains academic database services to researchers, journal editors and publishers. SIS focuses on: citation indexing, citation analysis, and maintains citation databases covering thousands of academic journals. SIS Provides Quantitative And Qualitative Tool For Ranking, Evaluating And Categorizing The Journals For Academic Evaluation And Excellence. This Factor Is Used For Evaluating The Prestige Of Journals. The Evaluation Is Carried Out By Considering The Factors Like Paper Originality, Citation, Editorial Quality, and Regularity & International Presence. We Perform The In-Depth Analysis Method. The Acceptance And Rejection Rates Of Journals Can Be A Determining Factor. Low Acceptance Rate, High Rejection Rate Journals Are Considered The Best And Most Prestigious Journals As The Acceptance Criteria Is Of High Quality Standard. Many Journals And Societies Have Web Pages That Give Publication Data And Style Requirements And Often Includes Acceptance/Rejection Rates. The Paper Copy Of The Journal Occasionally Includes This Data And Will Always Provide Current Contact Information. Whether A Journal Is Indexed In The Major Indexing/Abstracting Service In The Field Is Another Criteria That Can Be Used To Assess The Worth And Quality Of A Journal.
Sci-Hub :
Sci-Hub is a website that provides free access to millions of research papers and books, without regard to copyright, by bypassing publishers' paywalls in various ways.
Sci-Hub was founded by Alexandra Elbakyan in 2011 in Kazakhstan in response to the high cost of research papers behind paywalls. The site is widely used in both developed and developing countries, serving over 200,000 requests per day as of February 2016.
Sci-Hub and Elbakyan were sued twice for copyright infringement in the United States in 2015 and 2017, and lost both cases, leading to loss of some of its Internet domain names. The site has cycled through different domain names since then.
Sci-Hub has been lauded by some in the scientific, academic, and publishing communities for providing access to knowledge generated by the scientific community. Others have criticized it for violating copyright, threatening the economic viability of publishers, potentially compromising universities' network security and jeopardizing legitimate access to papers by university staff.
Electronic Journals Library :
The Electronic Journals Library is a service to facilitate the use of scholarly journals on the internet. It offers a fast, structured and unified interface to access full-text articles online.
It comprises 99764 titles from all areas of research, 21965 of which are available online only. In addition, 130244 journals, which are provided by aggregators, are listed. The EZB contains 64605 journals which are accessible free of charge to anyone. Furthermore, the participating libraries provide their users access to the journals they subscribe to.
The journals are presented in lists sorted by research area. An updated list is generated by the database according to the member library's specifications each time it is accessed.
Searchit:
Citeseerx:
Isindexing :
The ISI server provides indexing of major international journals and proceedings. Author can get information about international journal impact factor, proceedings (research papers) and information on upcoming events. All the journal pages have pointers to Web pages of the publishers which are integrated into the ISI stream pages.
The purpose is to increase the visibility and ease of use of open access scientific and scholarly journals. If your journal is indexed & got validated stamp from ISI, you can request for the calculation of impact factor for your journal.
ISI is a service that provides access to quality controlled Open Access Journals. The ISI aims to be comprehensive and cover all open access scientific and scholarly journals that use an appropriate quality control system, and it will not be limited to particular languages or subject areas. The aim of the ISI is to increase the visibility and ease of use of open access scientific and scholarly journals thereby promoting their increased usage and impact.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Iris Publishers-Open access Journal of Hydrology & Meteorology | Influence of Community Resilience to Flood Risk and Coping Strategies in Bayelsa State, Southern Nigeria
Authored by Nwankwoala HO *, Abstract This study is aimed at assessing the influence of community resilience to flood risk and coping str...

-
Authored by Nwankwoala HO *, Abstract This study is aimed at assessing the influence of community resilience to flood risk and coping str...
-
Authored by Shams Mohammed Noman *, Abstract Background: The purpose of the current study is to describe clinical manifestations, manage...
-
Authored by Mahmut Nedim Aytekin Abstract Lower extremity length difference causes orthopedic pathologies as well as a...









