Introduction
The problems of energy saving and environmental safety in fuel and energy plants are still relevant. To solve them, water-fuel emulsions (WFE), for example, fuel oil + water, motor fuel + water, are appropriate [1-3].
WFE from fuel oil, diesel fuel (DF), heating oil, gas for various testing gives their savings, a noticeable increase in the resource of heat and energy aggregates, their efficiency by 2-3%, a significant reduction in the release of harmful gases. Radical purification of exhaust gases (EG) from NOx (by 90%) by catalytic regenerators requires costs of 40.70 $/kW of diesel power [2]. Are they in the feed to the diesel steam while reducing NOx emission only up to 70%.
For testing in the Navy and in other industries, water in the fuel engine has the following actions [1,2]:
• reduces the temperature and prevents the explosive combustion of fuel,
• smoothest the dynamics of gas pressure in the cylinder,
• increases the average pressure in the cylinders,
• increases the completeness of fuel combustion,
• increases efficiency, does not reduce power, but slightly reduces engine acceleration,
• accelerates the conversion of CO to CO2,
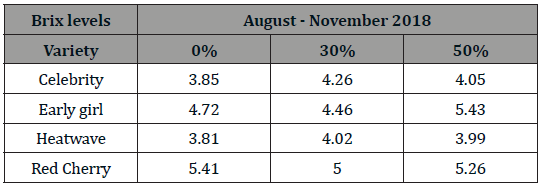
• reduces to EG soot, NOx and to a much carcinogenic benzopyrene С20Н12 (Figure 1) [1],
• cleans the combustion chamber from soot, ensures the operation of the engine in a gentle mode, reduces wear, vibration, noise.
• Water, as a component of motor fuel, has been tested in the world practice by various methods [1-6], including:
• direct injection into the cylinders of internal combustion engines (ICE), which from the pre-war until recently was used in aircraft engines;
• supply of dispersed water to the intake manifold of the internal combustion engine by a separate device or a separate carburetor;
• humidification of the fuel-air mixture, the formation of water-air or steam-air mixture before it is fed into the intake duct of the engine;
• formation of a water-fuel emulsion and its introduction into the fuel tank of machines [7-10].
According to the first technique is known, for example, a method of water injection into the cylinders of the internal combustion engine according to the pa-tent RU No. 2069274. Its drawback - the complexity of the regulation of water supply and the lack of formation of highly water-fuel mixture.
In the second technique known amateur ways of water flow from the micro-channels after the throttle valve of the carburetor, as well as tractor Fordson-Puti-lovets with additional water carburetor.
According to the third method, there are several ways of humidifying the air or fuel-air or preparing an air-water mixture. So, you know spraying water in the intake tract of the internal combustion engine before the carburetor (patent RU No. 2092709)
Another (patent RU No. 2136942) is the saturation of the fuelair mixture by water vapor produced by the heat of exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. Here the disadvantage is the need for an efficient steam generator and relatively low energy performance of water vapor. Analogues of this method are protected by patents of the RF No. 2094642, No. 2352805.
The disadvantage of all three methods of humidifying the fuel-air or creating a water-air mixture is that they do not give an adjustable composition of the highly dispersed fuel-air mixture, as well as energy indicators of the fuel-water-air mixture, which are underestimated in comparison with pure fuel.
On the fourth reception there are many ways of cooking WFE outside of the internal combustion engine, which consists in the preparation of 15-20% of water, of fuel, of the complex substances from emulsifiers, stabilizers, catalysts, combustion, and further their joint stirring. Here are a variety of patents SU No. 699005, 816524, 816524, 1230470, 1243342, 1246593, patent RU No. 2213768, patent RF No. 2294448, US patents No. 3807973, 1498340, 1533158, 1701621, 1701691, 3876391, 4199316, 4244702. 4696638. The disadvantages of entering the water in the internal combustion engine according to the above patents is the difficulty of techniques and tools for the creation of WFE and its lack of stability.
Patent of RF No. 2306447, 2365618, 2367683 for WFE use two groups of substances. In the 1st low molecular weight anionic surfactant and nonionic surfactant in a ratio of 3:1 to 6:1. In the 2nd stabilizing hydrophobiator and a high-molecular surfactant. In the 3rd polar organic solutions from betaine, propanol-2, sorbitol, oil distillate. In the 4th oil-compensating agents.
Examples of emulsifying system under patent No. 2365618 [9] for 76% of diesel fuel and 23% of process water emulsifying system (1% by weight. % to water) includes:
• component 1 - anionic surfactants (alkilsulfates of the general formula), 6,5%; nonionic surfactant (sorbifolia), 2%;
• component 2 - polyolefins (poly-alpha-olefins), 8,7%;
• component 3 – betaine, 3%;
• component 4 - nitrated oil, 6%.
Oil compensating agent apply engine oil or their promoters, providing or facilitating the lubrication of, for example, tributyl phosphate, tridecanol, tricar-bonyl, industrial diethylene triamine, poly-4-methylphenten-1, phosphate esters, thioether dialkyldithiophosphoric acid.
There is a similar version of the emulsifying system for benzowater emulsion.
These complexes of substances provide stability of WFE for up to 72 hours. However, the empirical selection of emulsifying and auxiliary substances (up to 33 substances), as shown by the testing of their cars in publications and patents, still does not provide longterm (up to 3 months) stability of WFE.
Described this mechanism of combustion of water-fuel emulsions [2]. The fuel oil from the injectors has a droplet size of 0.1 to 1mm. If they included a drop of water 1.7 microns, when heated, they give couples. It breaks a drop of fuel, increasing its dispersion, the surface of contact with air. In the high-temperature combustion zone, a drop of WFE explodes, a drop of fuel is dispersed secondarily, the combustion torch increases and reduces the local the maximum of temperatures in the chamber. It is clear that in comparison with the dispersed droplet of a large particle, the radiation area and the heat flux are smaller, burn lengthwise and not fully. At WFE with a uniform distribution of dispersed water, the size of fuel particles is reduced by 1.5…2.5 times, the combustion conditions and efficiency are also improved, the under burning of fuel is reduced, the volume of blast is reduced to an indicator of 1,0 and heat loss with it. The temperature of the dew point of the outgoing gases decreases to 100 °C significantly reduces sulfuric acid corrosion and increases the efficiency of energy and heat units, although it increases the emission of SOx into the atmosphere.
But WFE after storage is less effective than prepared immediately before combustion and without emulsifiers, giving carbon deposits in the ICE. In addition, ensuring long-term stability WFE is possible only with its careful and time-consuming preparation. Therefore, the 80s in Russia, and abroad, successfully operating installation direct feed of WFE in a variety of marine diesel engines, boilers, steam generators. The units have been tested on Russian and foreign trac-tors, MAZ and KamAZ vehicles, confirmed fuel economy up to 10-15%, and on stationary power units up to 40%. The installation is simple, has no moving parts except the pump and energy flow, which is provided by cyclical effects on WFE.
The Moscow institute VIESH also conducted research of water-fuel mixtures for many years. Here [3] it is believed that the activation of a mixture of water and hydrocarbons creates new phases of substances stabilized by electrostatic forces from induced charges. Because of them, free radicals appear in the mixtures, which allows to realize low-temperature combustion, significantly reduce the formation of incomplete combustion products, increase the service life and efficiency of the ICE. The authors [3] conducted, for example, such studies:
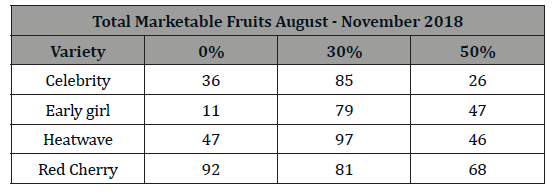
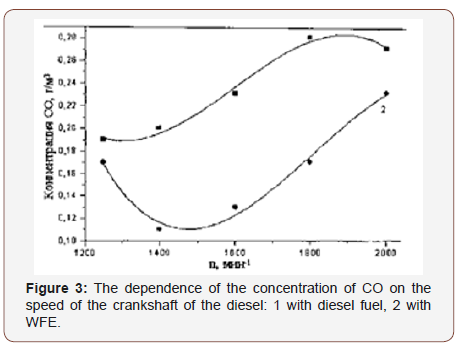
Testing of diesel YaMZ-238L on fuel with 20% water (St. Petersburg, Institute of Technology, 19.04.2007, Figures 2,3)
Indicators exhaust gas of the internal combustion engine with WFE in Figures 2,3 review is not required.
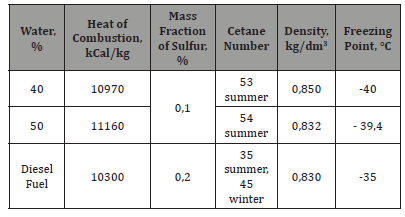
Studies of the emulsion of diesel fuel and water (Table 1)
As can be seen from Table 1, even with a water content of 40 and 50%, WFE in all respect’s superior to standard diesel fuel.
Table 1: Emulsion parameters with water content up to 40% [3].
Investigation of the molecular spectrum of WFE from 60% DF and 40% water
From the spectrograms of water and WFE on the spectrometer «Bruker AVANCE-300» follows:
• WFE spectrum consists of groups of signals, corresponding to CH3, CH2 and CH – groups and of groups of signals, corresponding to aromatics,
• signals, corresponding to water molecules, are not detected.
• comparison of the spectrograms of WFE and tap water [3] showed completely new properties of fuel from WFE, where water is not detected.
• So, in WFE a mixture of organic matter was detected, and the water dissolved in it was chemically bound. Similar results were obtained by other researchers.
• Special originality combustion WFE described Zavgorodny B.V. [2]:
• in addition to the improved atomization and mixing of fuel with air due to the vaporization and explosion of water droplets is also termocandelaria of its molecules: 2Н2О > Н2 + 2НО, as well as 2Н2О > 2Н2 + О2,
• therefore, the beginning of the oxidation of fuel molecules is more real products of water decomposition than air oxygen; fuel needs an instant rate of oxidizer, it gives an instant thermal decomposition of water molecules at 1500 °C; thus, 60% of the oxygen from the WFE is used to ignite the fuel in areas, in-accessible to air oxygen,
• hydrogen from dissociated water diffuses into a zone with excess oxygen and compensates for the costs of the heat of combustion for the dissociation of water,
• water vapor increases the volume of combustion products per H/4 kMol of water, which increases the work of gases in the cylinders of the engine.
The changing dynamics of combustion of WFE are shown on indicator diagrams of internal combustion engines [2]. Here, the expansion line is separated from the compression line by a greater distance, the average pressure increases, combustion is completed earlier by 30° of rotation of the crankshaft, the exhaust gas temperature decreases by 6.8 °C, the heat density of the cylinders decreases, the oil in them is less saturated with combustion products, which increases reliability, reduces engine wear. The acceleration of combustion, thanks to the products of water dissociation, ensures its completeness and environmental friendliness. The annual economic effect of only reducing fuel consumption on ships is $15 per 1 kW of power of the main diesel [2].
The above allows us to consider WFE as a special type of fuel.
However, the creation of a stable WFE is a difficult problem. WFE should be resistant to coalescence and sedimentation for at least 72 hours in the operation of the engine, at least a month in its parking lot, at least 3 months in addition, it should provide a lower cost of fuel. But water and hydrocarbons are not soluble in each other. Conventional emulsifiers make them only limited soluble. Thus, in long-term storage there are unclear chemical reactions even with change of coloring of WFE.
At physical influence on water change of its state only briefly because of high mobility of molecules. Hydrogen bonds between them are changeable, molecules with high frequency change their neighbors. In addition, the changeable properties of water and the presence of salts, gases, organic matter. The so degassed water is saturated with them again for a long time. And under the action of cosmic and other radiations free radicals and many other formations are formed in it [2,3], so WFE can change its properties.
Hence, it is clear that the preparation of homogeneous, highly stable WFE as a motor fuel is a difficult task, confirmed by many unsuccessful attempts to create it. Because only in Russia it will be tested at 19 firms.
The purpose of research: To develop methods for the preparation of a stable water-fuel emulsion, that meets the requirements for motor fuels containing a large volume of water, to check its fractional composition, stability and dynamics of the composition in storage.
Conditions, materials and methods: Two batches of unique WFE were pre-pared from 65% diesel fuel, 33% water and 2% emulsifiers, namely from previously studied 10 organic substances [6,8-10], which are included in two different functional groups. In the 1st - hydrophobic substances soluble in diesel fuel, introduced into it and mixed in it. In the 2nd of the substances with hydrophilic, soluble in water, injected into it and stir it. Fuel with its mixed emulsifiers, and water with other mixed emulsifiers were drained together and pumped for at least 5 minutes at a flow rate of 10cm/s through a combined static mixer-activator un-der RF patent No. 2411074. Further, the obtained WFE was controlled chemically, especially for compliance with the regulations for motor fuels and on the chromatograph «Crystallux-4000M» with the PID-PFD detector in the certified Tambov laboratory of forensic medical examination. After a long exposure of WFE its composition on the xromatograph was checked again. Conducted comprehensive operational testing of WFE in a diesel car «Mitsubishi Pajero» 1995 issue. And bench motor tests of WFE at three replications conducted on diesel YaMZ- 236.
Results and Discussion
The formation WFE was accelerated and strengthened by the introduction of stabilizers [6,8-10], consisting of oils, acid esters with a high viscosity index, auxiliary substances from hydroxides, alcohols, esters. Chemmotology and chromatography of the obtained WFE showed: density 897 kg/m3, flash point not lower than 67 °C, filterability temperature not higher than 5°C, corrosion on the copper plate in class I does not show, the sulfur con-tent according to the method RF GOST 32511-2013 corresponds to RF GOST 305.
A comparison of the compositions of WFE and diesel fuel detected on the chromatograph is given in Table 2. It follows from:
1. The proportion of light hydrocarbons in WFE (without taking them into account in the complex of the activated DF «Euro» and the DF from the Institute VNIITiN) until С15Н32 more than in activated DF «Euro» and considerably more than in unactivated fuel «Euro». And the share of heavy hydrocarbons in WFE, starting with C16H34, is significantly less than in inactivated and activated fuel «Euro».
2. Modification of fuels and WFE is explained by the processes of mechano-chemistry, going in the activator under patent No. 2411074. And the continuation of the modification outside the activator (the last column of Table 2), revealed in the 2000s in the Tomsk scientific center, has no proper explanation. It is assumed that it is caused by long-lived active radicals formed in the activator. A physicist Yu.P. Rassadkin and ecologist Drunvalo Melchizedek explain this by the influence of high-energy substances on low-energy ones.
The prevalence of lung and a lower content of heavy components in the WFE and in the activated DF, exposed for 57 days, has extraordinary character and testifies to high efficiency of the activator according to the patent of RF No. 2411074, which was confirmed by his tests on the engines KamAZ-740, JaMZ-236 and ZMZ-406.
The resulting 14.12.2017 WFE withstood until April 2018, again subjected to chromatography, which, like activated DF (last column of Table 2), showed the immutability of the properties of WFE. A comparison of the spectrograms DF and WFE showed the superiority of WFE over DF in fractional composition and without signs of water presence, as in the complex fuel of the Institute of VIESH [3].
Table 2: Comparison of content in WFE and DF.
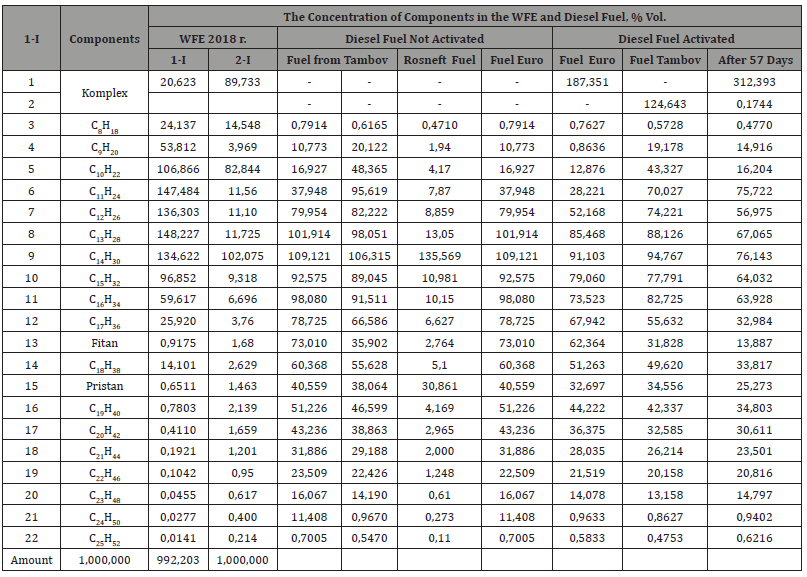
It should be noted that as if don’t detected water content in WFE can be explained by the fact that water molecules, as the most universal ligands, form complex compounds with fuel molecules, similar to gas hydrates, having specific spectral characteristics.
WFE has remained stable, without separation to 25.01.2019. And the car «Mitsubishi Pajero» is used only on this WFE. At the same time, the morning launch of the ICE was carried out on the 3rd attempt, and after trips on the 1st. The engine works softer, fuel consumption and noise of work decreased, acceleration of the car is normal. There are no negative phenomena in the work of the ICE.
Method of Solution
In this section, the DQM is used to solve the equations. In DQM, we can express the derivative of a function at a given point as a weighted linear summation of the values of the function at all the points in the domain [29]. Therefore, the differential equation can be transformed into a set of algebraic equations expressed by the value of the function at the node. When using this method, there are two questions to be determined:
Conclusion
Studies conducted in Russia and in many other countries, as well as successful testing of WFE on automotive diesel engines, have convincingly shown that WFE can be an environmental fuel for different types of transport. It corresponds to the unique composition and stability of WFE, obtained by the technology of TSTU. It is mainsheet consumption of diesel fuel by 9%, costs 25 rub./l.
To know about Open Access Publishers