Authored by Md Shariful Islam*
Introduction
Expansive clays are considered as a problematic due to high shrinkage and swelling potential. Expansive clays swell considerably when water is added to them and then shrink with the loss of water. Many civil constructions and foundations are subjected to large uplifting forces caused by swelling and shrinkage problems. These forces impact heaving, cracking and the breakup of both building foundation and slab-on-grade members. Expansive clays cover large parts of the United States, South America, Africa, Australia, India and a little portion of Bangladesh. There are little amount in research and investigation on swelling and shrinkage problems of expansive clay which are performed in Bangladesh. For Bangladesh it can be considered as a great significant data study due to its engineering significance, it has drawn attentions to many researchers and designers. Many innovative techniques are developed to counteract the problems posed by expansive soils by transformation of soil index properties with the addition of chemicals such as cement, fly ash, lime or combination of these, often alter the physical and chemical properties of the soil including the cementation of the soil particles. Especially use of lime or sand admixture has proved to have a great potential as an economical method for improving the geotechnical properties of expansive soils. These methods are quite effective in controlling the volumetric changes in expansive soils. Apart from the above techniques, geosynthetic inclusions as a technique of random reinforcement have also been found quite effective in controlling swelling and shrinkage [1]. Compacted expansive soils, reinforced with polypropylene fibres, have exhibited reduced tension cracking and controlled volumetric changes due to swelling and shrinkage [2]. Shen SL, et al. [3,4] observed that fibre inclusions increased the tensile strength. A combination of fly ash and polypropylene fibres has also been found to reduce the swelling and shrinkage characteristics of expansive soils [5-7]. Yilmaz I, et al. [8] observed that an increase in fiber content led to a reduction in the swelling potential of lime-stabilized clayey soil. Al-Muhaidib et al. [9] investigated the effect of two types of fibres (natural and synthetic) on the swelling properties of clayey soils. Jamsawang P [10] presented that the swell-consolidation characteristics of remoulded expansive clay specimens reinforced with randomly distributed nylon fiber. The secondary consolidation characteristics of both unreinforced and fiber-reinforced specimens also studied. It should be mentioned here that there are quite a few differences between the work done by [9].In this paper, two types of soil samples been considered, and soil has been collected from two different locations of Bangladesh. One is Ghodagari in Rajshahi that is the north part of Bangladesh and another is Gazipur in Dhaka that is the east part of Bangladesh. The main objectives of this paper is to evaluate the swellingconsolidation and unconfined compression characteristic of fiberreinforced of two different remolded expansive soils. This paper presents that the effective in controlling the volumetric changes in two expansive soils by using polysynthetic (Garment waste). This fiber chooses due to locally available and economical in Bangladesh. This fiber also uses as a recycling purpose. It also presents the comparison the swell-consolidation and unconfined compression characteristics of two different types of remoulded expansive clays specimens reinforced with randomly disturbed of polysynthetic (Garment waste). The odeometer test (one-degree consolidation test) of both unreinforced and reinforced specimens were observed. It should be mentioned that there is a little bit difference between the work done by Jamsawang P [10]. The fibre content presented in Jamsawang P [10] ranges from 0% to 0.3% that time nylon fibre was considered whereas this paper presents that one type of fibre (polysynthetic (Garment waste) and the ranges from 0% to 2%. The aspect ratios(l/d) considered in this paper were only 15 which is similar to Jamsawang P [10].
Swelling potential and swelling pressure
The term swelling potential is generally used to indicate the amount of vertical swell (expressed as percentage of initial sample thickness) obtained under a particular surcharge (usually 1psi).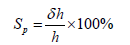
δh = amount of vertical swell
h = initial height
The swelling pressure is defined as the vertical pressure required to prevent volume change of laterally confined sample when it is allowed to take in water. Percent expansion decreases with increase in confining pressure for a given initial moisture content and density.
To read more about this article....Open access Journal of Civil & Structural Engineering
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/ctcse/fulltext/effect-of-garment-wastes-on-swell-consolidation-characteristics-of-expansive-soil.ID.000525.php
To know more about our Journals....Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers





No comments:
Post a Comment