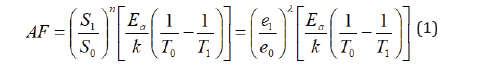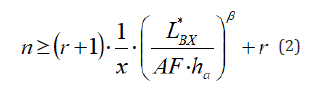Introduction
This work highlights the physics and metaphysics of the universe (multiverse) according to Paul C. Mocombe’s theory of phenomenological structuralism. The author posits that phenomenological structuralism offers an emergent metaphysical materialist account regarding the formation and perpetuation of the multiverse, consciousness, and society. Paul C. Mocombe’s structurationist theory of phenomenological structuralism, building on and synthesizing a form of M-theory with, mathematical elements of univon multiverse hypothesis, the quantum computation of ORCHOR theory, structurationism, and the multiverse ideas of Haitian ontology/epistemology and quantum mechanics abductively posits that consciousness is a fifth force of nature, a quantum material substance/energy, psychion, the phenomenal property, qualia or informational content, of which is recycled/entangled/ superimposed throughout the multiverse and becomes embodied via the microtubules of brains and multiple worlds to constitute mind. Mind, in turn, is manifested in simultaneous, entangled, superimposed, and interconnecting material resource frameworks, multiple worlds, as praxis or practical consciousness of organic life, which in-turn becomes the phenomenal properties, qualia, of material (subatomic particle energy, psychion) consciousness that is recycled/entangled/superimposed throughout the multiverses. In this sense, the physics of phenomenological structuralism posits an emergent materialist multiverse that is superimposed and entangled like consciousness.
Background of the Problem
Two views regarding the origins and nature of consciousness and the universe dominate contemporary physics. On the one hand, are theorists who view consciousness as fundamental to the universe and a by-product of a supernatural or cosmic creator who fine-tuned the universe for life and intelligent beings [1]. On the other hand, are materialists/physicalists who view our universe as a random product of chance among a plethora of multiverses some of which have life while others do not. Consciousness, in the latter, is simply a product of the mechanical and chemical processes of the brain imposing meaning onto a meaningless and absurd universe and the world.
Both positions are problematic when it comes to understanding the constitution of consciousness and the universe/multiverse. The former presupposes that consciousness in the form of a creator created the multiverse, and beings with consciousness are a perception in the mind of said creator (s). The latter assumes that consciousness is simply a chemical illusion of the mechanical brain interacting with matter. Although this latter position gives a mechanical understanding regarding the constitution of the universe/multiverse, it fails to explain the “hard problem” of consciousness (David Chalmers’s term), i.e., the subjective experiences of consciousness. For me, building on Paul C. Mocombe’s [2] metaphysical materialist theory of phenomenological structuralism, consciousness is emergent and comes to constitute a fifth force of the multiverse, with phenomenal properties, qualia, following matter random constitution, evolution, and disaggregation from the original four forces of nature, i.e., the weak and strong nuclear forces, gravity, and electromagnetism. In other words, consciousness is an emergent fifth force of nature, a quantum material substance/energy, psychion, the phenomenal properties, qualia, of which are recycled/entangled/superimposed throughout the multiverse and becomes embodied via the microtubules of brains and multiple worlds to constitute mind. Mind, in turn, is manifested in simultaneous, entangled, superimposed, and interconnecting material resource frameworks, multiple worlds, as praxis or practical consciousness of organic life, which in-turn becomes the emergent phenomenal properties, qualia, of material (subatomic particle energy, psychion) consciousness that is recycled/entangled/superimposed throughout the multiverses following matter disaggregation. Consciousness from this understanding is emergent and material following the constitution of space/time, which is fundamental.
In the human sphere, consciousness refers to subjective awareness of phenomenal experiences (ideology, language, self, feelings, choice, control of voluntary behavior, thoughts, etc.) of internal and external worlds emerging in space/time. The academic literature “describes three possibilities regarding the origin and place of this (human) consciousness in the universe: (A) as an emergent property of complex brain neuronal computation, (B) as spiritual quality of the universe, distinct from purely physical actions, and (C) as composed of discrete ‘proto-conscious’ events acting in accordance with physical laws not yet fully understood” [3]. The latter position, (C), represents the ORCH-OR (“orchestrated objective reduction”) theory of Stuart Hameroff and Roger Penrose (2014), which includes aspects of (A) and (B), and posits that “consciousness consists of discrete moments, each an ‘orchestrated’ quantum-computational process terminated by… an action [,objective reduction or OR,] rooted in quantum aspects of the fine structure of space-time geometry, this being coupled to brain neuronal processes via microtubules” (pg. 70). In this view, the understanding is that a proto-conscious experience existed in the universe, panpsychism, and as a result of emergent structures of the brain it (proto-conscious experience, psychion) became embodied and evolved as a result of quantum neuronal computations of “brains.” “Brains”, in the human form, as a part of the universe/multiverse, are used to both experience being-in-theworld and to capture the nature of reality as such in the form and emergence of the practice and language of science.
Paul C. Mocombe’s [4] structurationist sociology, phenomenological structuralism, which attempts to resolve the structure/agency problematic of the social sciences, builds on the ORCH-OR theory and panpsychism of Hameroff and Penrose, while holding on to the multiverse hypothesis of quantum mechanics (M-theory and the mathematics of univon multiverse hypothesis) and Haitian ontology/epistemology, which the authors reject because it is not “a more down-to-earth viewpoint,” to capture the nature and constitution of the universe/multiverse as such. (Hameroff and Penrose, [2]. For Mocombe [4], quantum superposition, entanglement, wave-function realism, and evidence in Haitian Vodou of spirit possession, which represent ancestors from a parallel world, Vilokan, of the earth’s of which we ought to pattern our behaviors and structures, are grounding proofs for the acceptance of the multiple worlds hypothesis of quantum mechanics. Within the latter hypothesis, the understanding is that “each possibility in a superposition evolves to form its own universe, resulting in an infinite multitude of coexisting ‘parallel’ worlds. The stream of consciousness of the observer is supposed somehow to ‘split’, so that there is one in each of the worlds—at least in those worlds for which the observer remains alive and conscious. Each instance of the observer’s consciousness experiences a separate independent world and is not directly aware of any of the other worlds” (Hameroff and Penrose, 2014, pg. 50). It is within this multiple world hypothesis, physics, that Mocombe constitutes his understanding of the emergence of the material multiverse and the notion of consciousness in each of the universes according to his theory of phenomenological structuralism. For Mocombe, consciousness is an emergent fifth force of nature, a quantum material substance/energy, psychion, the phenomenal properties, qualia, of which are recycled/entangled/superimposed throughout the multiverse and becomes embodied via the microtubules of brains. It (consciousness) is manifested in simultaneous, entangled, superimposed, and interconnecting material resource frameworks as mind or embodied praxis or practical consciousness, which in-turn becomes the phenomenal properties, qualia, of material (subatomic particle energy, psychion) consciousness that is recycled/entangled/superimposed throughout the multiverses following matter disaggregation [5-10].
In other words, I adopt from the “membrane theory” model of Lisa Randall and Raman Sundrum (1999) the assertion, in keeping with the logic of Haitian Vodou, that there might be an additional dimension on the cosmological scale, the scale described by general relativity, which gives rise to four dimensional multiverses within it. Our universe is embedded in a vastly bigger five-dimensional space (the four-dimensional space of relativity, plus a fifth dimension for the subatomic forces including consciousness), a kind of super-universe. Within this super-space, our universe is just one of a whole array of co-existing universes (Haitian Vodou only accounts for our universe and its parallel), each a separate fourdimensional bubble within a wider arena of five-dimensional space where consciousness (a subatomic force) is recycled/entangled/ superimposed between the species of the five-dimensional superspace, i.e., superverses, and their four-dimensional multiverses Figure 3.
The origins of consciousness and the multiverse within this phenomenal structural paradigm is emergent, and not the product of a supreme creator or god. For this position, I build on the mathematics of Richard Gauthier (2020) in his “univon multiverse hypothesis.” Unlike Gauthier, who holds on to God or a supreme creator to account for the origins and nature of consciousness within the multiverse, I do not. According to Gauthier’s (2020) model, identical univon quantum particles, produced from a univon quantum field, created not only our universe but also many other identically fine-tuned universes in a multiverse. The univon, also called a cosmic quantum, is composed of a helically circulating superluminal primordial information quantum (sprinq). [(The univon is the quantum particle of a conscious cosmic quantum field having both physical and mental potentialities. Quantum fields may be composed of cosmic ectoplasm or mind-stuff, which according to yoga philosophy is a subtle vibrational substance formed from consciousness by a cosmic creative power, that takes the form of objects within a cosmic mind)]. The physical [(and mind-stuff)] constants carried in the information content of each univon’s sprinq are exactly the same in all univons and in all sprinqs, though sprinqs express different fundamental particle attributes in different environments. The univon is radioactive. The decay of a univon into less energetic products is the starting point (t=0) of its created universe. The univon’s sprinq rapidly multiplies itself into different quantum fields and particles, leading very quickly to the early universe’s exponentially-rapid inflationary period and then to the Big Bang, which produces abundant relic dark matter particles of the universe as well as the less abundant ordinary matter. Univons made many other [(entangling)] equally fine-tuned universes with identical fundamental forces and constants…. (pgs. 1-3).
In my metaphysical materialistic model, which differs in language and the need for a “cosmic mind,” the “univon” is the cosmological scale described by Einstein constituted by the forces, constants, particles, etc., sprinqs in Gauthier’s hypothesis and phenomenal properties or qualia in my model, of the multiverses, with gravity and the psychionic force of consciousness emergent forces following matter aggregation, evolution, and disaggregation, which give rise to inflation, big bangs, and additional (entangled) universes with similar informational (physical and mental) content. Hence, the mathematics for both models are the same as seen in Figures 1 and 2, which is adopted from Gauthier (2020). I tie this physical model to Mocombe’s structuration theory, phenomenological structuralism, to explain the emergence and constitution of the multiverses, consciousness, minds, and society in them (Figure 1,2).
To read more about this article......Open access Journal of Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
https://irispublishers.com/abeb/fulltext/the-physics-of-phenomenological-structuralism.ID.000591.php
To know more about our Journals...Iris Publishers