Authored by T Karski*,
Abstract
The biomechanical causes of the “Idiopathic Scoliosis”, in new description “So-Called Idiopathic Scoliosis” - were described in years 1995-2007 in Lublin, Poland, but the observation and research was from 1984. All old conception about etiology were never correct because had no answered to all questions about “idiopathic scoliosis”. In my research I found that etiology is based / conneted on biomechanical factors-“permanent standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg” and walking / gait. These two biomechanical factors appear because of the asymmetry of hips movement-in right hip is limited adduction and often internal rotation and extension-in straight position of right hips. The restriction of movement of the right hip is one of the eight symptoms of the “Syndrome of Contracture and Deformities (SofCD) according to Prof. Hans Mau and Lublin observations. The found etiology give the possibility to describe the classification, rules of therapy and prophylactics.
Keywords: Scoliosis; Biomechanical etiology; New classification; Therapy; Prophylaxis
Introduction
Importance in etiology of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis. [Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)].
In the years 1984-1995, in examination of many children (N- 2500), I found that scoliosis is connected with the asymmetrical movement of hips and next with function-permanent “standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg” and “gait”. The limitation of adduction of the right hip, or even abduction contracture of this joint 5 to 10 degree is one of the symptoms of “The Syndrome of Contractures and Deformities” [SofCD] according to Prof. Hans Mau from Tübingen, Germany [1-18] and Lublin observations [19–29]. The straight position in examination is similar to the “standing position” or to the “stance phase in walking” and these “moments” play deciding role in development of scoliosis through function-“standing” and “gait” (Figure 1). The deciding is-that “standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg” is permanent because is safe, light, comfortable, stabile (words of children) and because of this the right leg is taken for standing (Figure 1).
Additionally causes in development of scoliosis
In many children with scoliosis can appear “neurological dysfunctions” and there are connected with the Minimal Brain Dysfunctions (MBD) in children from complicated pregnancy or delivery. In some scoliosis children I could see:
a. Extension contracture of trunk-here we should remember that in “S” scoliosis in 1st epg group/type and in “I” scoliosis in 3rd epg group/type-the spine is stiff in “extension position”,
b. Anterior tilt of pelvis-diminish stability between pelvis and spine-enable easy development of scoliosis,
c. Laxity of joints - easy development of scoliosis.
Material. In the years 1984-2019, more than 2500 patients with scoliosis were observed and treated. In all these cases I could found the asymmetry of the movement of the hips-limited adduction of the right hip in extension position of the joint. The control group-350 children-were presented by parents with the question about scoliosis-in these all cases the movement of hips was symmetrical and was no spine deformity [30-38].
Historical dates about etiology of scoliosis
• 1995-first lecture about biomechanical etiology of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis during Orthopedic Congress in Szeged, Hungary.
• 1996-first publication about biomechanical etiology of scoliosis in Orthopädische Praxis in Germany: T. Karski [1996] Kontrakturen und Wachstumstorungen im Huft- und Beckenbereich in der Ätiologie der sogenannten „idiopatischen Skoliosen”-biomechanische Überlegungen, Orthopädische Praxis 32, 3 (1996) 155-160
• 2001 and 2004-describing in new classification three etiopathological groups (epg) and four types of scoliosis: 3a/ “S” scoliosis in 1st epg, 3b/ “C” and 3c/ “S” scoliosis in 2nd epg., 3d/ “I” scoliosis in 3rd epg. In this type the spine is stiff, there are no curves or small ones.
• 2006-the ultimate description of the “type of hips movement” and the “type of scoliosis”.
• 2007-description of indirect influences coming from Central Nervous System (CNS) in children with Minimal Brain Dysfunction (MBD) and explanation the question-why the fool blind children have no scoliosis. Answer: their gait is without lifting of legs, with all time stable pelvis and standing is on the both legs with symmetrical loading.
New classification-Three groups and four types of scoliosis (Figure 1) [8 - 28]
The type of spine deformity is connected with “model of hips movement” and etiological factors-“gait” and “standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg”.
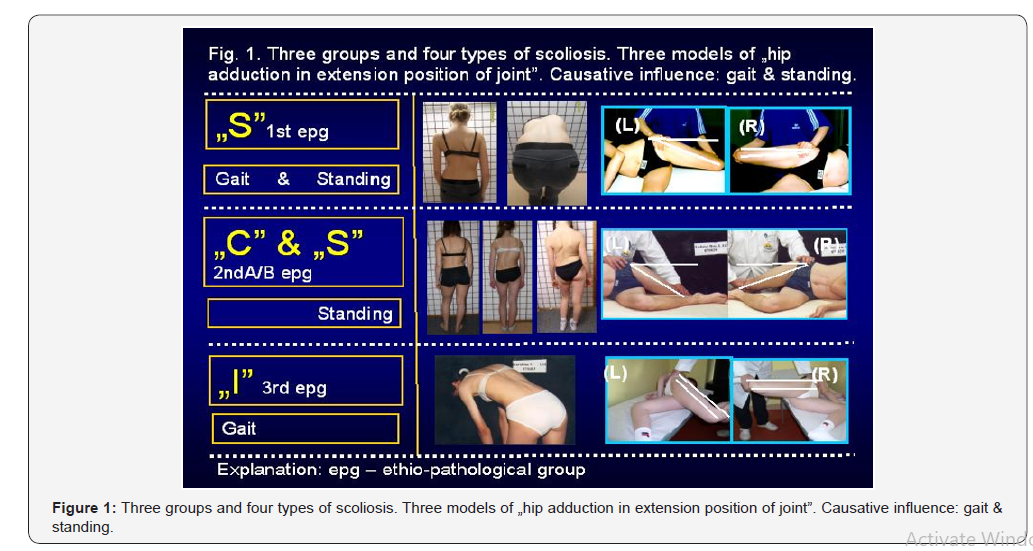
1. Scoliosis 3D - “S” 1st etiopathological group (epg) - double curve. Stiff spine. Rib hump on the right side of the thorax. Specific model of hip movements-maximally limited movement of right hip and full movement of the left hip. Connection with “gait” and permanent “standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg”. Mostly-rapid progression.
2. Scoliosis 1D or 2D - “C” 2nd/A epg-one curve-lumbar left convex. Flexible spine. Specific model of hip movementsminimally limited movement. of the right hip and full movement of the left hip. Connected with permanent standing „at ease’ on the right leg. This type of scoliosis is without progression.
3. Scoliosis 2D or 3D “S” 2nd/B epg-two curves. Specific model of hip movements-minimally limited movement of the right hip and full movement of the left hip. Connection with permanent standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg and additionally with laxity of joints or / and previous, harmful exercises. In the 2nd/A and 2nd/B types of scoliosis - the spine is flexible. This type of scoliosis is with moderate progression.
4. Scoliosis 2D or 3D - “I” 3rd epg. Specific model of hip movements-maximally limited movement of right hip and maximally or partially limited movement of the left hip. Deformity has the form of a stiff spine. No curves or small ones. The only cause is gait. Clinical symptoms are “stiffness of the spine in children” and “pain syndromes in adults”. Stiffness, like in the 1st type of scoliosis, is connected with “distortion movement” of intervertebral joints of the spine in every step during gait [39-41].
Test in Scoliosis
In diagnosis of scoliosis there are important old test but very important are new ones.
• Asymmetry of waist (old).
• Adams test-“bending test for scoliosis” (old).
• Lublin test-“side bending test for scoliosis” (new).
• Checking the adduction and internal rotation of the both hips in extension position of joint-especially of right hip (new).
• Checking of flexion contracture of hips (new).
• Checking of habit of standing-‘at ease’-on left or on right leg (new).
• Checking of “possible laxity of joints” (old and new).
Proper therapy (Figure 2)
In therapy there are very important flexion exercises - stretching exercises for hips-especially for right hip-for spine to cure the all “contracture” regions– its mean shortening of soft tissues-muscles, fascias, tendons, capsules of joints. All these exercises are similarly or the same like in karate, taekwondo, aikido, kung fu or yoga. Here I would like to inform that flexion exercises in the treatment of scoliosis in Poland (1960-1970) were introduced by Prof. Stefan Malawski from Warsaw / Otwock (31-33 and personal discussions).

Causal prophylaxis from the 4-5 years of life
• Standing at ease only on the left leg,
• Sitting in “butterfly position” (term from karate) and with relaxed spine-never straight up,
• Sleeping in the embryo position,
• Active participation in sports at school and additionally in clubs - the best are karate, kung fu, taekwondo, aikido, yoga,
• Physiotherapy / Kinesio-therapy to obtain full, symmetrical movement of both hips and movements of the spine-flexion, deviation, rotation.
• Especially important is to recover the full adduction and internal rotation movement of the right hip. It is new important aim for physiotherapy.
Conclusion
• The etiology of the so-called idiopathic scoliosis is strictly biomechanical.
• The pathological “model of hip movements” plays an important role in the development of scoliosis (T. Karski, 2006) and influence coming from function-“standing ‘at ease’ on the right leg” and “gait”.
• There are three groups and four types of scoliosis-see “new classification”.
• The children in/at the world wait for new therapy and causal prophylaxis in the So-Called Idiopathic Scoliosis.
To read more about this article...Open access Journal of Orthopedics Research
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
To know more about our Journals...Iris Publishers
To know about Open Access Publishers





No comments:
Post a Comment