Authored by Stefan Perisanu*,
Abstract
The reported values for the enthalpies of formation of α-amino acids in crystalline and ideal gas state are critically examined. Experimental values obtained by means of combustion calorimetry of the solid are compared with values calculated by means of group additivity. The ideal gas enthalpies of formation obtained by combining the solidstate values with the standard sublimation enthalpies are compared with ones calculated both additively and by means of quantum chemistry methods.
Keywords: Enthalpy of Formation; Amino acid; crystalline; Ideal gas; Calculated
Introduction
Numerous attempts were made during the last 90 years (a few were made even before) in order to determine the value of the parameter characterizing the stability of a molecule i.e. the enthalpy of formation, for an extremely biochemically important class of compounds, the amino acids. The proteinogenic L-α-amino acids were most investigated but the DL-stereoisomer was used in many cases, as well. The existence of differences between the enantiomers was also of interest. The aim of this paper is to present a state of the art of the existence of reliable values of standard enthalpies of formation in crystalline and ideal gas state for 27 α-amino acids.
Table 1:Experimental and calculated standard enthalpies of formation of L-α-amino acids*
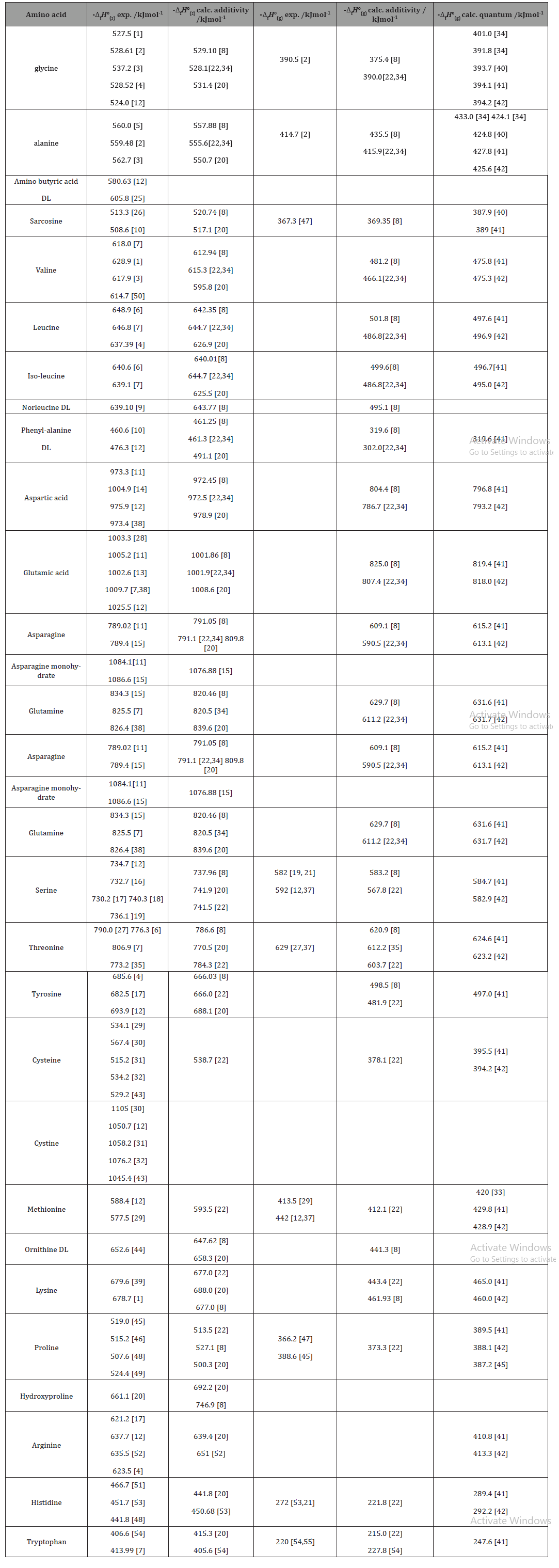
Discussion
Experimental values of enthalpies of formation in crystalline state obtained by means of heats of combustion in bomb calorimeters are shown in the second column of Table 1. The next column contains values of the same quantity calculated additively by means of contributions of groups of atoms. The fourth column contains values of the gas phase standard enthalpy of formation obtained from its value in solid state and the standard state heat of sublimation. Two kinds of calculated values of the gas phase enthalpy of formation are available. The first one is based on group additivity and the second on quantum chemical calculations (last two columns respectively) (Table 1).
*All data refer to the L- enantiomers if not specified otherwise.
For about 17 of the investigated amino acids at least two values of experimental solidstate enthalpies of formation agree fairly well (within a range of 4 kJ/mol). Divergent values of different authors are met for 8 molecules. A single reported value is available in the case of 2 amino acids. Calculated solid state enthalpies of formation of mono and dicarboxylic acids reported in references [8,22,34] are in good agreement with most experimental data. The calculated values with group contributions recommended by [20] are frequently less negative than experimental ones for monocarboxylic acids but not for dicarboxylic. The behaviors of asparagine and glutamine are particular. Asparagine has the tendency to build a monohydrate, while glutamine unlike most amino acids melts before decomposing. Some discrepancies between experimental and calculated values may be due to the inability of group additivity schemes to take into account all hydrogen bonds existing inside the crystalline lattice of a certain amino acid. A reasonable agreement between experimental and calculated values is observed also for hydroxy-amino acids, but not for all heterocyclic and sulfur containing ones. The experimental values for the ideal gas state standard enthalpy of formation are much scarcer than for the crystalline state. This is because the vapor pressure of amino acids at 298 K is very low so that most measurements were done at higher temperatures. Consequently most reported standard state heats of sublimation are extrapolation values. With the very limited number of reliable experimental values it is impossible to evaluate the performance of different calculation methods for the standard enthalpy of formation in gaseous state.
Conclusions
Reliable data for the standard enthalpy of formation in crystalline state of α-amino acids are available. Group additivity calculations are used as a tool for checking the quality of experimental data and in order to correlate the thermochemical quantities with material’s structure. A considerable amount of research remains to be done in order to have a comprehensive image about the ideal gas state enthalpy of formation of most compounds of this class. A special effort has to be done in order to valorize the existing data about heats of sublimation by using performing methods of obtaining its value at the standard temperature.
To read more about this article....Open access Journal of Chemistry and Biochemistry
Please follow the URL to access more information about this article
To know more about our Journals...Iris Publishers





No comments:
Post a Comment